File - Farrell`s Class Page
... Organism’s behaviors are responses to environmental stimuli. As individuals differ in their experiences, they will acquire different behaviors, and subsequently, different personalities. Changing environmental conditions can influence a person for the better. Therefore, personality is not st ...
... Organism’s behaviors are responses to environmental stimuli. As individuals differ in their experiences, they will acquire different behaviors, and subsequently, different personalities. Changing environmental conditions can influence a person for the better. Therefore, personality is not st ...
Slajd 1
... social context as well as individual personal choices. Each person is motivated differently, and will therefore act on his or her environment in ways that are unique. ...
... social context as well as individual personal choices. Each person is motivated differently, and will therefore act on his or her environment in ways that are unique. ...
Chapter 9: Motivation and Emotion
... The Motivation of Hunger and Eating: Environmental Factors Food availability and related cues Palatability: people eat more when the food available tastes good to them. Quantity available: people eat more when more food is put in front of them. Variety: people eat more when there is a greater varie ...
... The Motivation of Hunger and Eating: Environmental Factors Food availability and related cues Palatability: people eat more when the food available tastes good to them. Quantity available: people eat more when more food is put in front of them. Variety: people eat more when there is a greater varie ...
Foreword
... regulated learners in terms of a cyclical model of self-regulation that links metacognitive processes, behavioral performance, and motivational beliefs in three successive phases: forethought, performance, and selfreflection. Descriptive research regarding expert performance and experimental resear ...
... regulated learners in terms of a cyclical model of self-regulation that links metacognitive processes, behavioral performance, and motivational beliefs in three successive phases: forethought, performance, and selfreflection. Descriptive research regarding expert performance and experimental resear ...
5 Behavioral Theories of Learning
... Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice Chapter 5 Behavioral Theories of Learning This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: • any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; • preparatio ...
... Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice Chapter 5 Behavioral Theories of Learning This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: • any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; • preparatio ...
Four
... • Defined -- the application of aversive or unpleasant consequences to a behavior. A punishment reduces the likelihood of a behavior occurring. • Like a negative reinforcer, it is unpleasant but a negative reinforcer strengthens and sustains behaviors. Punishment/Discipline weakens and eliminates be ...
... • Defined -- the application of aversive or unpleasant consequences to a behavior. A punishment reduces the likelihood of a behavior occurring. • Like a negative reinforcer, it is unpleasant but a negative reinforcer strengthens and sustains behaviors. Punishment/Discipline weakens and eliminates be ...
HUMAN BEHAVIOR IN ORGANIZATIONS Block 3: Nature, Theories
... -positive reinforcement results from the application of a positive consequence following a desirable behavior. - the operation of presenting a positive reinforcer contingent upon a response is called positive reinforcement. Example: A student who studies deligently receives favorable consquences in ...
... -positive reinforcement results from the application of a positive consequence following a desirable behavior. - the operation of presenting a positive reinforcer contingent upon a response is called positive reinforcement. Example: A student who studies deligently receives favorable consquences in ...
Sample Lecture: "Feedback Reinforcement and Intrinsic Motivation"
... that will happen as a result ...
... that will happen as a result ...
Learning/Behaviorism
... processes in operant conditioning • Tolman’s hungry rats • Memory processes store the learning – Not all learning is an immediate behavioral response to a stimulus or potential consequence ...
... processes in operant conditioning • Tolman’s hungry rats • Memory processes store the learning – Not all learning is an immediate behavioral response to a stimulus or potential consequence ...
Understanding Motivation
... _______________ refers to the person that needs more arousal than the average person. Psychological factors that are included in motivation includes: incentives, cognitive dissonance, and psychosocial needs. Incentive theory has the belief that our attraction to particular goals or objects mot ...
... _______________ refers to the person that needs more arousal than the average person. Psychological factors that are included in motivation includes: incentives, cognitive dissonance, and psychosocial needs. Incentive theory has the belief that our attraction to particular goals or objects mot ...
MOTIVATION Motivating people is not an easy task. What motivates
... flow experiences. An interesting task for further research relates to the development of intervention methods: volitional strength may be depleted but can be built up by exercise. That leads us to virtues and leadership competencies, based on behavioral habits. 2.3. Outcome theories Outcome theories ...
... flow experiences. An interesting task for further research relates to the development of intervention methods: volitional strength may be depleted but can be built up by exercise. That leads us to virtues and leadership competencies, based on behavioral habits. 2.3. Outcome theories Outcome theories ...
chapt. 10 ppt.
... • Low motivation when one feels they have little or no control over work environment. • Ability to set and achieve clear goals can increase job performance and satisfaction. • Especially effective goals are: ▫ Personally meaningful. ▫ Specific and concrete. ▫ If supported by management. ...
... • Low motivation when one feels they have little or no control over work environment. • Ability to set and achieve clear goals can increase job performance and satisfaction. • Especially effective goals are: ▫ Personally meaningful. ▫ Specific and concrete. ▫ If supported by management. ...
Leading Through Motivation
... motivational stimulus originates outside the person. INTRINSIC REWARDS are self-administered; they occur "naturally" as a person performs a task. The feelings of competency, personal development, and self-control people experience in their work. ...
... motivational stimulus originates outside the person. INTRINSIC REWARDS are self-administered; they occur "naturally" as a person performs a task. The feelings of competency, personal development, and self-control people experience in their work. ...
Chapter 4 Developmental
... Infancy/Childhood—brain development; maturation and motor development Cognitive development—Piaget and 4 stages of cognitive development—basic info Social development—Harlow’s theory, describe attachment theory and types of attachment, temperament and attachment Deprivation of attachment Erikson sta ...
... Infancy/Childhood—brain development; maturation and motor development Cognitive development—Piaget and 4 stages of cognitive development—basic info Social development—Harlow’s theory, describe attachment theory and types of attachment, temperament and attachment Deprivation of attachment Erikson sta ...
Pengelolaan Organisasi Entrepreneurial
... – Explain differences between social learning theory and reinforcement theory – Discuss how self-managing can be useful in developing a motivation program – Describe how expectancy, equity, and goal-setting theories are used to motivate employees ...
... – Explain differences between social learning theory and reinforcement theory – Discuss how self-managing can be useful in developing a motivation program – Describe how expectancy, equity, and goal-setting theories are used to motivate employees ...
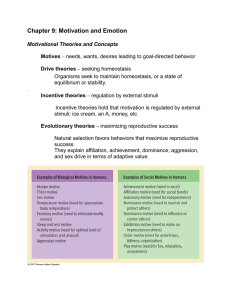
Drive theories
... MotivationThe psychological process that arouses, directs, and maintains behavior. NeedA motivated state caused by physiological deprivation (such as a lack of food, water, etc.) DriveAn internal aroused condition that directs an organism to satisfy some physiological need. ...
... MotivationThe psychological process that arouses, directs, and maintains behavior. NeedA motivated state caused by physiological deprivation (such as a lack of food, water, etc.) DriveAn internal aroused condition that directs an organism to satisfy some physiological need. ...
T10_Motivation_(2009-2)_web
... getting things done. Volunteer services are scarce and more people expect higher salaries because of greed. Unlike intrinsic motivation, which comes from inside, extrinsic motivation is created from external factors. ...
... getting things done. Volunteer services are scarce and more people expect higher salaries because of greed. Unlike intrinsic motivation, which comes from inside, extrinsic motivation is created from external factors. ...
Equity Theory
... Conditioning Theory • Operant Conditioning – People learn to perform behaviors that lead to desired consequences and learn not to perform behaviors that lead to undesired consequences. – Linking specific behaviors to the attainment of specific outcomes (such as pay raises or recognition) can motivat ...
... Conditioning Theory • Operant Conditioning – People learn to perform behaviors that lead to desired consequences and learn not to perform behaviors that lead to undesired consequences. – Linking specific behaviors to the attainment of specific outcomes (such as pay raises or recognition) can motivat ...
Motivation - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... learned/nurtured needs for achievement, power, and affiliation B. Need for fairness is another important motivational factor C. Intrinsic versus extrinsic motivation 1. Intrinsic motivation comes from enjoyment in doing the activity or work itself 2. Extrinsic motivation comes from factors outside o ...
... learned/nurtured needs for achievement, power, and affiliation B. Need for fairness is another important motivational factor C. Intrinsic versus extrinsic motivation 1. Intrinsic motivation comes from enjoyment in doing the activity or work itself 2. Extrinsic motivation comes from factors outside o ...
Educational Psychology Essay assignment Ch1
... Explain how children’s explanations for success and failure (i.e., their attributions) are likely to influence their thoughts and behaviors, and identify ways in which teachers can help children make accurate and productive ...
... Explain how children’s explanations for success and failure (i.e., their attributions) are likely to influence their thoughts and behaviors, and identify ways in which teachers can help children make accurate and productive ...
Industrial and Organizational Psychology
... Work behavior determined by two classes of needs Hygiene factors, rewards and social factors Motivator factors, nature of work Theory says only motivator factors can motivate work performance One of the few theories abandoned based on data ...
... Work behavior determined by two classes of needs Hygiene factors, rewards and social factors Motivator factors, nature of work Theory says only motivator factors can motivate work performance One of the few theories abandoned based on data ...