Behaviorism
... Time out – removing a person form a rewarding situation, e.g. sitting in the corner after misbehaving in class. Extinction – withholding reinforcers for target behaviors, e.g. looking away from a client when he talks “off topic.” Stimulus control – removing a stimulus that triggers undesired behavio ...
... Time out – removing a person form a rewarding situation, e.g. sitting in the corner after misbehaving in class. Extinction – withholding reinforcers for target behaviors, e.g. looking away from a client when he talks “off topic.” Stimulus control – removing a stimulus that triggers undesired behavio ...
Guided Reading Questions Unit 6
... 15. What is learned helplessness? How does it relate to predictability? ...
... 15. What is learned helplessness? How does it relate to predictability? ...
Motiv-iipm
... Motivation begins with the presence of a stimulus (psychology) that spurs the recognition of a need. Need recognition occurs when a perceived discrepancy exists between an actual and a desired state of being ...
... Motivation begins with the presence of a stimulus (psychology) that spurs the recognition of a need. Need recognition occurs when a perceived discrepancy exists between an actual and a desired state of being ...
Module 21 Operant Conditioning
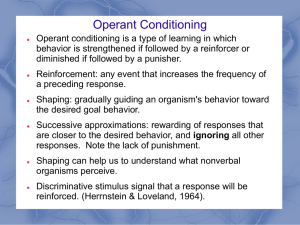
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
File
... • Punishment suppresses the behavior only so long as the delivery is guaranteed. For example, if parents are inconsistent with punishment, children learn very quickly how to “get away with murder” with one parent and not the other. • Punishment may be imitated as a way of solving problems. Thus, a c ...
... • Punishment suppresses the behavior only so long as the delivery is guaranteed. For example, if parents are inconsistent with punishment, children learn very quickly how to “get away with murder” with one parent and not the other. • Punishment may be imitated as a way of solving problems. Thus, a c ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint Pres.
... • Punishment suppresses the behavior only so long as the delivery is guaranteed. For example, if parents are inconsistent with punishment, children learn very quickly how to “get away with murder” with one parent and not the other. • Punishment may be imitated as a way of solving problems. Thus, a c ...
... • Punishment suppresses the behavior only so long as the delivery is guaranteed. For example, if parents are inconsistent with punishment, children learn very quickly how to “get away with murder” with one parent and not the other. • Punishment may be imitated as a way of solving problems. Thus, a c ...
Behaviorism
... – Punishment can involve adding something (paying a fine, staying after school) or involve removing something you like (losing recess time, leaving your friends) – In both cases, adding something or removing something, you perceive it as “bad” and as a result, you exhibit the behavior less. ...
... – Punishment can involve adding something (paying a fine, staying after school) or involve removing something you like (losing recess time, leaving your friends) – In both cases, adding something or removing something, you perceive it as “bad” and as a result, you exhibit the behavior less. ...
Famous Experiments
... What happens? Greater # of people in group, slower people are to respond to help ...
... What happens? Greater # of people in group, slower people are to respond to help ...
Coaching Children to Embrace a
... Acceptance and approval by adults and peers strongly influence children's perceptions of competence, enjoyment, and motivation. Coaches can make an impact on these elements in several ways. First, they can provide frequent and contingent informational feedback on how to improve skills. The term cont ...
... Acceptance and approval by adults and peers strongly influence children's perceptions of competence, enjoyment, and motivation. Coaches can make an impact on these elements in several ways. First, they can provide frequent and contingent informational feedback on how to improve skills. The term cont ...
Module 22 - operant conditioning
... Immediate & Delayed Reinforcers 1. Immediate Reinforcer: A reinforcer that occurs closely to a behavior in time. Rat gets a food pellet for a bar press. 2. Delayed Reinforcer: A reinforcer that is delayed in time for a certain behavior. A paycheck that comes at the end of a week. ...
... Immediate & Delayed Reinforcers 1. Immediate Reinforcer: A reinforcer that occurs closely to a behavior in time. Rat gets a food pellet for a bar press. 2. Delayed Reinforcer: A reinforcer that is delayed in time for a certain behavior. A paycheck that comes at the end of a week. ...
Ch 8 Jeopardy Answers
... A behavior that spreads from one situation to a similar one. This type of schedule of reinforcement is when a test is given every Friday. Learning to tell the difference between one event or object & another. Reverse of generalization. Learning that isn’t obvious; that takes place under the surface. ...
... A behavior that spreads from one situation to a similar one. This type of schedule of reinforcement is when a test is given every Friday. Learning to tell the difference between one event or object & another. Reverse of generalization. Learning that isn’t obvious; that takes place under the surface. ...
Chapter 17
... They may involve interim reinforcers if rule is followed (praise for sticking to a program leading to a larger reinforcer). The individual may make self-reinforcing statements in the interim. Following rules itself may be reinforcing due to our history of reinforcement for following rules in general ...
... They may involve interim reinforcers if rule is followed (praise for sticking to a program leading to a larger reinforcer). The individual may make self-reinforcing statements in the interim. Following rules itself may be reinforcing due to our history of reinforcement for following rules in general ...
Operant Conditioning
... A mental representation of the layout of one’s environment. For example, after exploring a maze, rats act as if they have learned a cognitive map of it. (Tolman) ...
... A mental representation of the layout of one’s environment. For example, after exploring a maze, rats act as if they have learned a cognitive map of it. (Tolman) ...
Picture from Ladies` Home Journal
... satisfaction to the animal will, other things being equal, be more firmly connected with the situation, so that, when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other things being equal, have their connections to th ...
... satisfaction to the animal will, other things being equal, be more firmly connected with the situation, so that, when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other things being equal, have their connections to th ...
9.2 Operant Conditioning
... Disadvantages of Punishment • 1.) Can produce unwanted side effects such as rage, aggression and fear. • 2.) People learn to avoid the person delivering the aversive consequences. • Punishment does not teach appropriate and acceptable behavior. Without positive coaching and modeling, the child may ...
... Disadvantages of Punishment • 1.) Can produce unwanted side effects such as rage, aggression and fear. • 2.) People learn to avoid the person delivering the aversive consequences. • Punishment does not teach appropriate and acceptable behavior. Without positive coaching and modeling, the child may ...
Classical Conditioning
... Behavior is reinforced because the subject receives something they want. ...
... Behavior is reinforced because the subject receives something they want. ...
document
... Figure 6.13 Intermittent reinforcement schedules Skinner’s laboratory pigeons produced these response patterns to each of four reinforcement schedules. (Reinforcers are indicated by diagonal marks.) For people, as for pigeons, reinforcement linked to number of responses (a ratio schedule) produces ...
... Figure 6.13 Intermittent reinforcement schedules Skinner’s laboratory pigeons produced these response patterns to each of four reinforcement schedules. (Reinforcers are indicated by diagonal marks.) For people, as for pigeons, reinforcement linked to number of responses (a ratio schedule) produces ...
Learning Perspective
... Evaluate any 3 pieces of key research from this perspective, each taken from a different theory. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of using Positive Reinforcement rather than punishment Describe what steps should ideally be considered if punishment is used. Explain any two organizations or gr ...
... Evaluate any 3 pieces of key research from this perspective, each taken from a different theory. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of using Positive Reinforcement rather than punishment Describe what steps should ideally be considered if punishment is used. Explain any two organizations or gr ...
Theories of Human Behavior Objectives
... suppressed and returns with punishment is no longer present; creates fear; only tells you what NOT to do, not what TO do. c. Social Learning: i. Observation Based ii. Role model demonstrates behavior, perceived by learner to be reinforced (or not) processing and representing in memory cognitive ...
... suppressed and returns with punishment is no longer present; creates fear; only tells you what NOT to do, not what TO do. c. Social Learning: i. Observation Based ii. Role model demonstrates behavior, perceived by learner to be reinforced (or not) processing and representing in memory cognitive ...
O.C. Day 1
... • Animals placed in puzzle boxes • String pulled, latch released, animal jumps out and receives food • Learning by random trial and error • Law of Effect – Thorndike’s principle that responses are “stamped in” by rewards and “stamped out” by punishments. ...
... • Animals placed in puzzle boxes • String pulled, latch released, animal jumps out and receives food • Learning by random trial and error • Law of Effect – Thorndike’s principle that responses are “stamped in” by rewards and “stamped out” by punishments. ...
vocab review unit 6 Learning
... • A neutral stimulus that after an association with an unconditioned stimulus (UCS), comes to trigger a CR. ...
... • A neutral stimulus that after an association with an unconditioned stimulus (UCS), comes to trigger a CR. ...
Ch.08 - Learning
... • Rewarding someone for doing something they already enjoy may cause them to lose their intrinsic interest in the task. Rewarding an already justifiable activity becomes “overjustified” because of the additional reward. ...
... • Rewarding someone for doing something they already enjoy may cause them to lose their intrinsic interest in the task. Rewarding an already justifiable activity becomes “overjustified” because of the additional reward. ...
Ch.07 - Learning
... • Rewarding someone for doing something they already enjoy may cause them to lose their intrinsic interest in the task. Rewarding an already justifiable activity becomes “overjustified” because of the additional reward. ...
... • Rewarding someone for doing something they already enjoy may cause them to lose their intrinsic interest in the task. Rewarding an already justifiable activity becomes “overjustified” because of the additional reward. ...