* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOCHEMISTRY
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
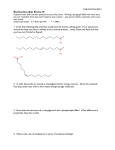
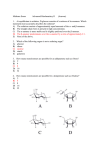
BIOCHEMISTRY CH 360 EXAM 3 November 30, 2007 There are six pages, NINE questions, and a total of 115 points in this exam. Please read each question carefully and possibly more than once. Good luck… (12) 1. Complete the following reactions by showing the full structures of the missing products. Please do not use abbreviations. 1.1. O O P O O O OH O P O O O kinase + ADP + ? ATP NH2 N O P 1.2. O O O P O O O O P O O N O N N adenylyl cyclase ? HO + OH (11) 2. The two compounds shown below resemble certain natural metabolites. What are these natural metabolites? In which metabolic pathways do they take part? What is the outcome of using the compounds below instead of the natural metabolites in the relevant metabolic pathways (you have chosen)? F OH 2- O3PO O O (a) O As O - O2C HO O (b) CO 2CO 2- ? (30) 3. Circle the best (only ONE) correct answer for the multiple choice questions given below: 3.1. The centers labeled (a) and (b) in the structure below are: (a) OH CO 2H HO 2C (b) (1) a-prochiral, b-prochiral (3) a-prochiral, b-chiral 3.2. (2) a-chiral, b-chiral (4) a-chiral, b-prochiral Which of the following sugars cannot be fermented or yield energy? (1) fructose (2) mannose (3) galactose (4) talose (5) all of the sugars above can be fermented and yield energy. 3.3. Which one(s) of the reactions below consume(s) energy in the form of reduction potential? Remember the correlation between NADH and ATP. Acetaldehyde Ethanol Pyruvate (a) ( (1) (a) 3.4. Pyruvate (b) (2) (b) (3) (a) and (b) Acetyl CoA (c) (4) (b) and (c) Fructose is much sweeter than glucose, but less abundant in nature. Therefore, in order to increase the sweetness of foods, glucose is converted to fructose (high fructose corn syrup) by heating to induce isomerization. Unfortunately, since the reaction goes to equilibrium, the glucose can never be completely converted. What enzymes might you use to completely convert glucose to fructose? (1) (2) (3) (4) 3.5. Lactate Phosphofructokinase, glucose-6-phosphate isomerase Hexokinase, glucose-6-phosphate isomerase Hexokinase, glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, fructose-6-phosphatase Hexokinase, glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, glucose-6-phosphatase Which of the following statements is correct? (1) (2) (3) (4) Under anaerobic conditions the conversion of glucose to pyruvate is much slower Glycolysis speeds up in the presence of oxygen since more ATP is produced under anaerobic conditions than in aerobic conditions. Glycolysis is slowed down in the presence of oxygen since more ATP is produced under aerobic conditions than in anaerobic conditions. The presence of oxygen does not effect the rate of glycolysis. . Page 2 3.6. Which is not a similarity between active transport proteins and enzymes? (1) (2) (3) (4) 3.7. Both undergo conformational changes upon binding a substrate Both are susceptible to inhibition Both can reach a saturation limit Both cause chemical modification to the substrate The toxins from cholera and whooping cough interfere with the proper functioning of which of the following? (1) G proteins (4) Protein kinase A 3.8. (2) isomerization (4) none of the above Caffeine potentiates the activation of the protein kinase A pathway because: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) 3.10. (3) ATP synthesis Transfer of the phosphoryl group from phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP) to ADP is an example of (1) a mutase reaction (3) a dehydrogenase 3.9. (2) DNA polymerase (4) all of the above it binds to the regulatory subunit of protein kinase A and promotes dissociation of the catalytic subunit it activates hormone receptors directly. it stimulates the GTPase activity of G proteins. it binds to target proteins and promotes phosphorylation by protein kinase A. it inhibits cAMP phosphodiesterase and prolongs the cAMP signal. Which of the following enzymes catalyzes a reaction which does not produce CO 2 in the citric acid cycle? (1) isocitrate dehydrogenase (3) -ketogluterate dehydrogenase complex (2) succinate dehydrogenase (4) pyruvate dehydrogenase (6) 4. During vigorous exercise, the cardiovascular system cannot deliver O 2 to the muscle tissue to maintain aerobic conditions. As glycolysis proceeds under aneorobic conditions, NAD + is converted to NADH; but the muscle tissue has no O2 to which NADH can pass electrons. To recycle NADH to NAD +, which is essential for continuing glycolysis, something must happen (as painful as it might be –hint… hint). Illustrate with a chemical reaction what happens at this point. Page 3 Inspired by a question from Stephanie (6) 5. In an isolated mitochondrion one turn of citric acid cycle can be accomplished using the starting materials shown below. O Br CO2 O2C 10.1. CO2 * * SCoA O2C O2C CO2 CO2 O2C What substance is accumulated in people who cannot produce enough insulin? CO2 CO2 aconitate Show where the indicated (starred) carbons from bromoacetyl-CoA would end up in aconitate. Note that there are three possibilities: (1) carboxylate and the adjacent methylene (2) carboxylate and the adjacent (unsaturated) methine (3) you cannot tell Rationalize your answer (this is where you will get the points!) (9) 6. During glycolysis, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate undergoes a reaction catalyzed by an aldolase enzyme to yield dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. Think of a monosaccharide which can undergo a similar reaction but gives two equivalents of identical products (without the need to undergo isomerization). Show the structure of the monosaccharide, its product(s) and a brief outline of mechanism. (Note that your monosaccharide can have as many carbons as you wish) (For a bonus of 5 pts you can also tell me which, and how many, stereoisomers of the monosaccharide you have chosen would work to give you two equivalents of identical products) Page 4 (16) 7. The standard reduction potentials (Eo’ ) for the following half reactions are given. FAD + 2H+ + 2e- FADH2 E0' = -0.219V Q + 2H+ + 2e- QH2 E0' = 0.045V 7.1. Determine the direction of the electron flow in the mitochondrion (from which coenzyme to which coenzyme) 7.2. Write a chemical equation which represents your answer for 7.1. 7.3. Show whether the passage of 2 electrons from one coenzyme to the other is sufficient to drive the synthesis of ATP from ADP (+30.5 kJ/mol energy needed) Show your work. No credit will be given for guesswork or for answers which are not based on quantifiable parameters. (The Faraday constant, F, is 96.5 kJ/V.mol) Page 5 (19) 8. Which carbon in glucose needs to be labeled in order to generate pyruvate labeled at C-1? If more than one carbon can be labeled to achieve the result above, identify both carbons. Show your work. 8.1. What is meant by “labeled carbon” and how can it be detected? (Remember there are more ways than one to label a carbon!) 8.3. What happens to the labeled carbon of pyruvate when it goes into the citric acid cycle? (trick question!) (6) 9. The following is a Linewever-Burke plot for isocitrate dehydrogenase, and phosphorylated isocitrate dehydrogenase. Explain why the plot looks this way. Page 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 11 30 6 6 9 16 19 6 0 0 TOT 115 Page 7