* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY - Georgia Institute of Technology
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
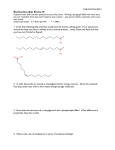
SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY Glycolysis 1 Announcements • Exam #2 on June 26 – Chapters 7, 8, 11, 12, 14 • Bring calculators • Study Session with Vonda – Thursday, June 26; 2-3:45 pm – Boggs 228 2 Introduction to Glycolysis • Glycolysis: breakdown of sugars • Primary start point = glucose • 10 enzymatic reactions 3 Overview Stage I of Glycolysis • 2 ATP’s invested • 1 Glucose is broken into 2 phosphorylated molecules 4 Overview Stage II of Glycolysis • 4 ATP’s recovered • 2 NADH’s produced • GAP is converted to pyruvate 5 Enzymes in Glycolysis Stage I: Energy Investment 1. Hexokinase • Uses ATP 2. Phosphoglucose Isomerase [PGI] 3. Phosphofructokinase [PFK] • Uses ATP 4. Aldolase • Splits 6C into two 3C molecules 5. Triose Phosphate Isomerase [TIM] 6 Enzymes in Glycolysis Stage II: Energy Recovery 6. Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase • 7. Uses NAD+ to form NADH Phosphoglycerate Kinase [PGK] • Forms ATP (2 molecules) 8. Phosphoglycerate Mutase [PGM] 9. Enolase • Forms high energy molecule 10. Pyruvate Kinase [PK] • Classify these on board Forms ATP (2 molecules) 7 Key Mechanisms • Kinases: Transfer PO32- to substrate • Phosphoglucose Isomerase • Aldolase • GAP Dehydrogenase • Phosphoglycerate Mutase 8 Example of Kinase Activity Step 1: Hexokinase 9 Phosphoglucose Isomerase Reaction Mechanism Step 2 10 PGI Reaction Mechanism Base Catalysis 11 PGI Reaction Mechanism Acid Catalysis 12 PGI Reaction Mechanism Base catalyzes ring closure H+ 13 Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Step 6 Remember: Glycolysis produces 2 molecules of GAP, and therefore 2 molecules of NADH 14 GAP Dehydrogenase Mechanism Free Enzyme 15 GAP Dehydrogenase Mechanism Thiol Addition 16 GAP Dehydrogenase Mechanism Dehydrogenation 17 GAP Dehydrogenase Mechanism Phosphate Binding Pi 18 GAP Dehydrogenase Mechanism 19 Phosphoglycerate Mutase 20 Phosphoglycerate Mutase Mechanism 21 Pyruvate Kinase 22 What happens to pyruvate? 23 PRS • What is the maximum number of O2 molecules that hemoglobin can bind? 1. One 2. Two 3. Three 4. Four 24 PRS • 1. 2. 3. 4. B cells mature in the ________. Thymus Bone marrow Muscle tissue Myosin 25 PRS • Oxygen binding to myoglobin results in what shaped curve? 1. Sigmoidal 2. Hyperbolic 3. Linear 4. Sinusoidal 26 PRS • Which of the following amino acids is not in the catalytic triad of serine proteases? 1. Ser 2. Thr 3. His 4. Asp 27 PRS • 1. 2. 3. 4. What is Km? The catalytic efficiency The catalytic rate constant 1/2 Vmax [S] at 1/2 Vmax 28