* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
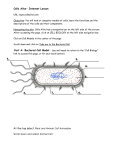
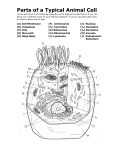
Name _______________________ Date: ____________ Hour: ______ Cells Alive- Internet Lesson - Go to: www.cellsalive.com Go to Contents and on the drop down menu click on CELL BIOLOGY. From here, you can access the links. Objective: To observe models of various cells and learn their components & functions. Part A: Click on Cell Models to access this page. Read the information in boxes and answer the questions below: 1. What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Click on the prokaryotic cell model and answer the following questions: 2. Label the prokaryotic bacterial cell below. 3. What substance is located in the nucleoid region of this cell? _________________ 4. Does this substance appear to be surrounded by a membrane bound nucleus? 5. What is the function of the ribosomes? 6. What is the function of the cell wall? 7. What are flagella, and what is their purpose? 1 Part B: Return to the "Cell Biology" link and click on “CELL MODELS”, then click on the eukaryotic cell picture, click “START THE ANIMATION” and choose then click on “Animal Cell” to access the information. For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to get the information. 1. Which organelle is the most obvious found in eukaryotic cells, but not in prokaryotic cells? 2. Do prokaryotic cells still have DNA? Sketch each of the following: Mitochondria 3. What do mitochondria do? 4. What are mitochondria comparable to in size? Lysosome 5. What does the Golgi Apparatus do? 6. What is the function of the smooth ER? Centrosomes (centrioles) 7. Where is the nucleolus found? 8. What does the nucleolus do? 9. What does the cytoskeleton do? Golgi Apparatus 10. What is the function of the lysosome? 2 Rough ER Part C: Return to “Plant and Animal Cell Animation” then click on “Plant Cell” to access the information. 1. What polysaccharide makes up the cell wall? Chloroplast 2. What organelle makes the plant cells green? 3. What is the function of the rough ER? 4. In plant cells, what does the vacuole do? Vacuole Part D: PROCEED TO CELL QUIZ! Go to: http://www.biologycorner.com/quiz/qz_cell_parts.html Write your answer to #1-10 from the cell quiz on the line as you go. Include your score at the bottom once it is corrected. 1. ___________________________ 6. ___________________________ 2. ___________________________ 7. ___________________________ 3. ___________________________ 8. ___________________________ 4. ___________________________ 9. ___________________________ 5. ___________________________ 10. ___________________________ Score (%) = _________ Part F: Concept Check: (No website) Place a check in the box if the cell has it! Use your notes and cells alive website to help you! Organelle Plant Animal Bacteria Organelle Plant Animal Bacteria 3 1. Chloroplast 7. Vacuole 2. Ribosome 8. Golgi Bodies 3. Mitochondria 9. Centrioles 4. DNA 10. Lysosomes 5. ER 11. Nucleolus 6. Cell Wall 12. Cell Membrane Part E: Molecular Transport: Diffusion & Osmosis Go to: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab1/concepts.html Complete the lab bench activity, by answering the questions and clicking the right button at the bottom of the page when done with the step. 1. What is diffusion? Click on term for definition! 2. What is osmosis? Click on term for definition! Take a closer look & ANIMATE 3. What does it mean for a molecule to move ‘down its concentration gradient’? Take a closer look & ANIMATE 4. What molecule appears to be larger… iodine or starch? 5. What happens when iodine and starch mix? 6. What is the movement of water influenced by? 4 7. What is a HYPOtonic solution? 8. What is a HYPERtonic solution? 9. What is an ISOtonic solution? 10. Will there be a net movement of water between two isotonic solutions? 11. What will happen to a red blood cell placed in distilled water? 12. Why doesn’t this happen to red blood cells in the bloodstream? 13. Why doesn’t this happen to plant cells? 5