* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monkemeier / Senko - Madison Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
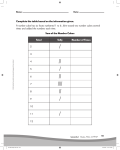
Monkemeier Honors Biology December 8, 2014 – December 12, 2014 Unit 4: Microscopes, Structure and Function of Cells NAME__________________________ DATE _________________ What Limits Cell Size? Minilab Activity This activity will answer the following questions: - Why can't cells continue to grow larger and larger to become giant cells, like a blob? - Why are most cells, whether from an elephant or an earthworm, microscopic in size? - What happens when a cell grows larger and what causes it to divide into two smaller cells rather than growing infinitely larger? - What limits cell size? Objective: Demonstrate that as a cell grows, the cell membrane does not increase in size as fast as the volume of a cell. Vocabulary: Define and / or provide mathematical models for the following terms.: Cell Membrane: Surface Area (of cell membrane): Volume (of the cell): Materials: Sand Scissors Tape Balance for measuring mass Cube A (smallest cube) = 1 unit Cube B = 2 units across Cube C = 3 units across Cube D = 4 units across Procedure: 1. Examine the four cubes. Notice that cube A is the smallest cube that there is a relationship between the four cubes. 2. Fill each of the four cubes to the top with sand. Place each cube on an electronic balance and measure the mass of each cube. Record the mass of each cube in the data table attached. 3. Calculate the total surface area for each cube. Do this by using the formula: Area = 6 x 2 (number of units across) . Record each area in the data table attached. 4. Calculate the total volume of each cube. Do this by using the formula: Volume = (number of units across)3. Record the volume of each cube in the data table attached. 5. Calculate the distance from the center of the cell to the center of each wall. Do this by using the formula: Distance = (number of units across) / 2. Record this for each of the four cells in the data table attached. Data Table: Cube Number of Units across 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 Total Surface Area: Volume Area = 6 x (number of units across)2 Volume = (number of units across)3 Distance from center to edge Distance = (number of units across) / 2 Mass of Cell Filled with Sand Surface Area / Volume Surface Area / mass (grams) Calculations: 1. Using the information in your data table, divide the total surface area by the volume for each cube. Record your “ratios” in the data table above. 2. Using the information in your data table, divide the total surface area by the mass for each cube, Record your “ratios” in the data table above. Analyzing the Data: 1. Anything that the cell takes in, like oxygen and food, or releases, such as carbon dioxide, must cross the cell membrane. Which measurement of the cells best represents how much cell membrane the models have? 2. The cell contents, nucleus and cytoplasm, use the oxygen and food while producing the waste. Which two measurements best represent the cell content? 3. As the cell grows larger and gets more cell content, will it need more or less cell membrane to survive? 4. As the cell grows larger, what happens to the Total Surface Area -to- mass ratio? 5. Why can't cells survive when the Total Surface Area -to- Volume ratio becomes too small? 6. Which size cell has the greatest Total Surface Area -to- Volume Ratio? 7. Which size cell has the greatest chance of survival? Explain your reasoning. Drawing Conclusions: Which ratio limits the cell size? (In other words, what limits how large a cell can grow?) Describe what happens when a cell grows and approaches the ratio mentioned in the prior question? What is the benefit of being composed of many specialized cells working together to perform specific functions rather than just being one big cell? Some unicellular organisms are described as colonial. Colonial organisms can join together to share common functions; however, each cell maintains its own identity. List some possible benefits to cells when involved within a colony. Scientists have evidence that multicellular organisms evolved from unicellular organisms. WHY is there a need for organisms to be multicellular rather than one very large cell? HOW do you think multicellular organisms evolved?