* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of a Cell Adapted
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
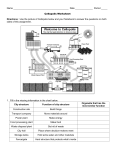
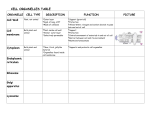
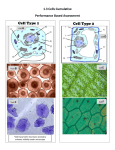
Name:_______________________ Date: __________________ Parts of a Cell Introduction Cells are the basic units of life found in both plants and animals. Cells must be able to carry out all life functions of the organism, such as making new materials and removing energy from food. Cells contain many parts with special jobs that work together to carry out these life functions. Organelles are small structures inside of cells that carry out specialized jobs. In this activity, you will learn the structure and the function of nine important cellular organelles. Organelles Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoplasm Vacuole Mitochondrion Nucleus Ribosome Lysosome Procedures: 1. Read pages 16-22 of Cells and Heredity (Prentice Hall Science Explorer) and complete the second (plant cell, animal cell, or both), third (location- where is it found), and fourth columns (function- what does it do) in the chart. 2. Sometimes, it is easier to remember new information when you compare it something you already know about. Comparing a new idea to an old idea is called making an analogy. Compare each of the seven cell organelles to a part of a city and fill in the fifth column of the chart. This will help you remember what each organelle does inside of a cell. You may choose from the list below or create your comparison. o o o o o o o o o City Hall Food Processing Plant City Storage Waste Disposal Plant Power plants Construction Site Bus and subway systems inside the city City Gate Border Patrol Check points Chart: Important Cell Organelles Organelle Is it in plant cells, animal cells, or both? Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Nucleus Ribosome Vacuole Lysosome Where in a cell is it located? What does this organelle do in the cell? Compare this organelle to a part of a city. Explain your choice. 3. Locate and label the nine cell organelles on the diagrams below. Keep in mind that not all nine organelles are present in all types of cells. Animal Cell Plant Cell Summary Questions 1. Which organelles are present in both animal and plant cells? __________________ ___________________ ______________________ _____________________ _____________________ ________________ 2. Which organelles are present only in plant cells? _______________ ________________ 3. Which organelles are present only in animal cells? ____________________ 4..List organelles that specialize in protecting the cell. _________________ _______________ 5. Some organelles are specialized to extract energy from food. List the organelle that help cells extract energy from food. _________________________ 6. Some organelles are specialized to make new materials. List organelles that help cells make new materials. ______________________ ____________________ (BONUS: _____________________________ ____________________________________) Specialized Cells in Plants and Animals Plants and animals are called multi-cellular organisms because they contain many cells. Some of the cells within plants and animals are specialized to perform specific functions. 1. View the two animal cells below. The first is a nerve cell and the second is a red blood cell. Both cells are found in humans, as well as in other animals. nerve cell red blood cells a) What do both cell types have in common? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ b) What is unique about the nerve cell? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ c) Nerve cells carry information between the brain and the rest of the body. How do you think their shape helps them carry out this function? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ d) What is unique about the red blood cells? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ e) Red blood cells roll through the blood carrying oxygen to all the parts of the body. How do you think their shape helps them carry out this function? 2. View the two plant cells below. The first is a leaf cell and the second is a root cell. a) The leaf cell has chloroplasts, but the root cell does not. Why do you think this is so? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ b) The root cell has root hairs, but the leaf cell does not. Why do you think this is so? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________