* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KEY to Cell Part Chart FUNCTIONS
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
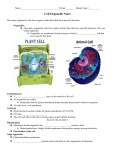
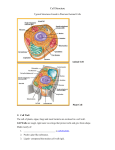
Honors Biology Name ________________________ Cell Part Chart Cell Part Structure (Diagram required) Function (What does it do?) Selectively permeable, phospholipid bilayer that controls the movement of material into and out of ALL cells. Cell Membrane Provides shape and support; contains cellulose in plants, chitin in fungal cells, peptidoglycan in bacterial cells. Cell Wall with Cellulose Location (No Diagram) Membrane-bound organelle that stores the DNA, RNA, and nucleolus of eukaryotic cells. Nucleus Site of ribosome production Nucleolus A linear molecule of DNA wrapped around proteins in non-dividing cells; controls protein production Chromatin Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton (No Diagram) Water-based solution that fills the area between the cell membrane and the nucleus of the cell; location of many cell organelles, the cytoskeleton, and many chemical reactions A network of protein filaments and tubules in ALL cells that provides internal support and helps to move materials within the cell and to move cells. Cell Part Structure Location Function Sites of proteins synthesis. Proteins intended to stay in the cell are synthesized by free-floating ribosomes. Ribosomes Mitochondria Membrane-bound organelle that is the site of aerobic respiration. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum A network of folded membranes-bound sacs that extend from the nuclear membrane and is studded with ribosomes; synthesizes proteins that will be exported to the Golgi body for processing. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum A network of folded membrane that extends from the nuclear membrane; synthesizes lipids. (R.E.R.) (S.E.R.) Golgi Body Vesicles Lysosomes Vacuoles (in animal cells) Flattened membrane-bound sacs that package proteins from the Rough E.R. into vesicles and help to metabolize lipids. Membrane-bound containers that transport materials within cells and out of cells. A membrane-bound vesicle that contain digestive enzymes to break down molecules within the cell. Membrane-bound containers that store water, wastes, and other materials. Cell Part Central Vacuole Centrioles Chloroplasts Chromoplasts Amyloplasts Structure Location Function A large membrane-bound container that occupies approx. 30-80% of the cells volume; Stores water and other materials and helps to maintain turgor pressure. Bundles of microtubules in animal cells that help to move chromosomes during cell division. Membrane-bound plant organelles that contains chlorophyll; Site of Photosynthesis Membrane-bound plant organelles that contains carotenoid pigments that create the orange, yellow, and red colors of plant parts. Non-pigment membrane-bound plant organelles that produce and store amylose (starch).