* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14 Guided Reading
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Alternative splicing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
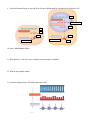
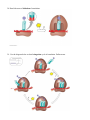
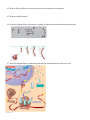
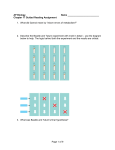
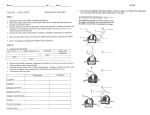
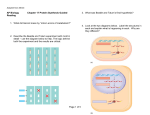
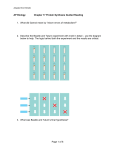
Name _________________________ Chapter 14: Gene Expression from Gene to Protein 1. What is a gene? 2. What is gene expression? Section 14.1 3. What did Garrod mean by “inborn errors of metabolism?” using alkaptonuria as an example. 4. Describe the Beadle and Tatum experiment with bread mold in detail and label the diagram below. The logic behind both the experiment and the results are critical. 5. What was Beadle and Tatum’s final hypothesis? 6. Use the diagram below to discuss Beadle and Tatum’s one gene, one protein hypothesis. 7. Give two examples of nonprotein enzymes and how Beadle and Tatum’s hypothesis had to be altered. 8. Define the role of each of the following in the production of a protein from DNA: a. Transcription b. Messenger RNA c. Translation d. Ribosomes e. Primary transcript 9. Label the diagram below to note the flow of genetic information in a prokaryotic & eukaryotic cell 10. State Crick’s central dogma 11. Why does the “code” have to be in triplets and not singles or doubles? 12. What is the template strand? 13. Label the diagram below illustrating the triplet code. 14. Compare and contrast the codon and anticodon? 15. How did Nirenberg “figure out” which amino acids went with which codes? 16. Using the codon table for mRNA, translate the following codons: a. UUC b. CAU c. AGG d. AUG e. UGA f. GAA 17. What is the reading frame? 18. What conclusions can be drawn from the similarities of the genetic code among living organisms? Section 14.2 19. Define the following terms relating to transcription: a. RNA polymerase b. Promoter c. Terminator d. Transcription unit 20. Use the diagram below to understand transcription: Label the diagrams and discuss what is happening. 21. Use the diagram below to demonstrate initiation of transcription at a eukaryotic promoter. Label all parts of the diagram and discuss what is occurring at each step.. 22. What is a TATA box? 23. To which end of the growing RNA strand will RNA nucleotides be added to? 24. Label the diagram below showing the elongation stage of transcription 25. How does termination differ between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? 26. What results from transcription in eukaryotic cells? Section 14.3 27. What is RNA processing and why is it necessary? 28. What does adding a 5’ cap and poly-A tail mean and why is it important? 29. Label the diagram below illustrating RNA processing of the pre-mRNA 30. Define the following terms: a. RNA splicing b. Introns c. Exons d. Alternating RNA splicing e. Spliceosome 31. Label the diagram below illustrating RNA processing/splicing 32. What is the role of ribozymes in RNA splicing? Section 14.4 33. Describe the structure and function of transfer RNA. 34. Label the diagram below showing the basic concepts of translation 35. Why is the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase important to translation and protein synthesis? 36. What is “wobble”? 37. Describe the structure and function on ribosomal RNA & label the diagram below. 38. Detail the steps of initiation of translation. 39. Use the diagram below to detail elongation cycle of translation. Define terms. 40. Now we are at termination. Label the diagram of termination below. 41. What was the role of GTP in all three processes in translation? 42. What is an example of a post translational modification of a protein? 43. Use the diagram below to highlight the signal mechanism for targeting proteins to the ER. 44. What is the key difference between prokaryotic and eukaryatic transcription? 45. What are polyribosomes? 46. Label the diagram below showing the coupling of transcription and translation in prokaryotes. 47. Label the diagram below summarizing transcription and translation in eukaryotic cells. Section 14.5 48. Define the following terms: a. Mutations b. Point mutations c. Nucleotide pair substitution d. Silent mutation e. Missense f. Nonsense g. Insertions h. Deletions i. Frameshift mutation j. Mutagen 49. How has a gene been “redefined” and why? 50. You will need to know the difference between all the gene mutations. Use the diagram below to familiarize yourself with the mutations.