* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prokaryotic cell information - Mrs-Dow
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
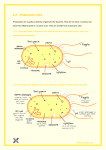
Biology AH –extra notes 2.2 Side 1 Prokaryotic cells All living things can be classified (grouped) according to the type of cells (building blocks) they are made up from. Cells can be divided into two main groups the prokaryotes, which are simple cells and the eukaryotes, which are more complex. The eukaryotes can further be divided in the following cell types protists, fungi, animal and plant cells. Below are characteristics of the different cell types. Prokaryotes Bacterial cells Single celled Naked DNA (DNA is not associated with protein) DNA is found free-floating in the cytoplasm usually as a single circular chromosome No membrane bound organelles 70S ribosomes (smaller sized ribosomes) Cell wall made up of peptidoglycan Eukaryotes Plants cells Usually exist as part of a multicellular organism DNA is associated with proteins (histones) Possess DNA enclosed within a nucleus Have many membrane bound organelles Autotrophic (manufacture their own organic molecules, food) Have chloroplasts for carrying out photosynthesis Cell wall made up of cellulose Animal cells Usually exist as part of a multicellular organism Possess DNA enclosed within a nucleus DNA is associated with proteins (histones) Have many membrane bound organelles Heterotrophic (consume complex organic molecules, food) Fungal Cells Usually exist as part of a multicellular organism DNA is associated with proteins (histones) Possess DNA enclosed within a nucleus Have many membrane bound organelles Cell wall made up of chitin Protist Cells Usually single celled DNA is associated with protein (histones) Possess DNA enclosed within a nucleus Some are autotrophic Some are heterotrophic Mrs Dow Biology AH –extra notes Side 2 Use the information given about each cell type to construct a dichotomous key that could be used to identify each cell type. 1. DNA is found free-floating in the cytoplasm ………Prokaryotic Cell (bacterial cell) Possess DNA enclosed within a nucleus………………………. Go to 2 2. Usually found as a single cell …………………………… Protist Cell Usually exist as part of a multicellular organism ………………Go to 3 Mrs Dow Biology AH –extra notes Side 3 2.2.1 Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of Escherichia coli (E.coli) as an example of a prokaryote. 2.2.2 Annotate the diagram with the functions of each named structure. The prokaryotic cell is the simplest type of living cell. They are relatively small having a diameter in the range of 0.5 to 5µm. A light microscope will only show the general shape of bacterial cells and does not have the magnification or resolving power to show the cell contents. To see the ultrastructure (the details of the cell contents) an electron microscope has to be used. Go to the following website: http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/bactcell.htm Draw a labeled diagram of a Prokaryotic cell. For each of the following structures annotate their functions: cell wall; plasma membrane; cytoplasm; pili; flagella; ribosomes and nucleoid region. Mrs Dow Biology AH –extra notes 2.2.3 Identify structures from 2.2.1 in electron micrographs of E. coli. Look at the micrographs below and label as many features as you can: Mrs Dow Side 4 Biology AH –extra notes Side 5 2.2.4 State that prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission. Bacterial Reproduction Prokaryotes are much simpler in their organization than are eukaryotes. There are a great many more organelles in eukaryotes, as well as more chromosomes to be moved around during cell division. The typical method of prokaryote cell division is binary fission, shown below. The prokaryotic chromosome is a single DNA molecule that first replicates, then attaches each copy to a different part of the cell membrane. When the cell begins to pull apart, the two chromosomes are separated. Following cell splitting (cytokinesis), there are now two cells of identical genetic composition (except for the rare chance of a spontaneous mutation). Binary Fission in Bacteria http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SLpFJ1JeRYs Mrs Dow Biology AH –extra notes http://www.rockefeller.edu/vaf/chain20.gif Mrs Dow Side 6