* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - TeacherWeb
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
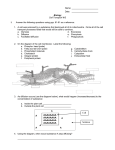
Name_____________________ Period_____ Date____________ Osmosis Worksheet STATEMENT Isotonic Cell(s) Hypotonic Hypertonic Cell(s) Cell(s) 1. The concentration of dissolved substances (stuff) in the solution is lower than the concentration inside the cell. 2. When a cell is placed in this solution, water will enter the cell by osmosis resulting in osmotic (turgor) pressure. 3. The concentration of dissolved substances (stuff) in the solution is the same as the concentration inside the cell. 4. The concentration of dissolved substances (stuff) in the solution is higher than the concentration inside the cell. 5. When this solution is injected into the body no cell disruption occurs because no net osmosis occurs. 6. Putting a plant in this solution will result in water loss and cause the plant to wilt. Why does a plant like celery get limp when placed in a hypertonic solution? Pure water is always what (Hypertonic, Hypotonic, or Isotonic) compared to any cell? Why? All of the cells have 20 water molecules and 2 sugar molecules. Please make sure all ratios are simplified! Simplify this ratio for 1 easy point. 12:4 becomes ___:____ SOLUTION A: 30 water molecules and 3 sugar molecules Cell Solution Beginning Ratio _____water molecules : _______ sugar molecules Ending Ratio _____water molecules : _______ sugar molecules 1. Is the solution hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic with regard to cell? 2. Is the cell hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic with regard to solution? 3. Will more water molecules leave the cell, enter the cell, or stay at the same ratio as they are at now? 4. Will the cell look the same, be shriveled, or be bursting after equilibrium has been reached? All of the cells have 20 water molecules and 2 sugar molecules. SOLUTION B: 30 water molecules and 12 sugar molecules Beginning Ratio _____water molecules : _______ sugar molecules Ending Ratio _____water molecules : _______ sugar molecules 5. Is the solution hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic with regard to cell? 6. Is the cell hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic with regard to solution? 7. Will more water molecules leave the cell, enter the cell, or stay at the same ratio as they are at now? 8. Will the cell look the same, be shriveled, or be bursting after equilibrium has been reached? All of the cells have 20 water molecules and 2 sugar molecules. SOLUTION C: 40 water molecules and 2 sugar molecules Beginning Ratio _____water molecules : _______ sugar molecules Ending Ratio _____water molecules : _______ sugar molecules 9. Is the solution hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic with regard to cell? 10. Is the cell hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic with regard to solution? 11. Will more water molecules leave the cell, enter the cell, or stay at the same ratio as they are at now? 12. Will the cell look the same, be shriveled, or be bursting after equilibrium has been reached?