* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transport WS - Kenston Local Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
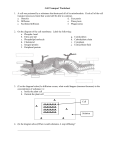
Name: _______________________ Date: _______________________ Biology Cell Transport WS I. Answer the following questions using pgs. 81-91 as a reference: 1. A cell was poisoned by a substance that destroyed all of its mitochondria. Circle all of the cell transport processes listed that would still be able to continue. a. Osmosis d. Exocytosis b. Diffusion e. Pinocytosis c. Facilitated diffusion f. Phagocytosis 2. On the diagram of the cell membrane: Label the following: a. Phospho- head (polar) b. Fatty acid tail (non-polar) g. c. Phospholipd molecule h. d. Cholesterol i. e. Integral protein j. f. Peripheral protein Cytoskeleton Carbohydrate chain Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid 3. As diffusion occurs (use the diagram below), what would happen (increase/decrease) to the concentration of substance: a. Inside the plant cell _________________________ b. Outside the plant cell _______________________ A A A A AAAAAAAA AA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA AAAAA Cell A Solution A 4. Using the diagram, when would substance A stop diffusing? ________________________________________________________________ 5. What would happen to a plant cell in each of the following solutions? a. Hypertonic: The cell would ____________________________ because the water molecules would _____________________. b. Hypotonic: The cell would _______________________________ because the water molecules would _______________________. c. Isotonic: The cell would __________________________________ because the water molecules would ______________________. 6. What would happen to an animal cell in each of the following solutions? a. Hypertonic: The cell would ____________________________ because the water molecules would _____________________. b. Hypotonic: The cell would _______________________________ because the water molecules would _______________________. c. Isotonic: The cell would __________________________________ because the water molecules would ______________________. 7. Complete the following sentences: a. A plant deprived of water will wilt because of a loss in __________________ pressure. b. The ability of a cell membrane to permit some substances to enter the cell and keep others out is known as _____________________________. 8. Compare the similarities and difference for the following terms: a. Phagocytosis & pinocytosis i. Same: ii. Different: b. Molecular Pump & facilitated diffusion i. Same: ii. Different: c. Exocytosis & endocytosis i. Same: ii. Different: d. Osmosis & diffusion i. Same: ii. Different: 9. If you are stranded on the ocean, why should you NOT drink salt water (a hypertonic solution)? Give your answer in terms of what you learned about cell transport. 10. When a hospital patient is given IV fluids, what tonicity should those fluids be and WHY?