* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4 Review KEY File
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
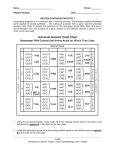
Test is on ______! Review is due on ____________ ! Name:_______________ Date: _____ Protein Synthesis & Mutations Test Review 1. Define point mutation. Change in a single nitrogen base of a DNA sequence 2. Define frameshift mutation. Addition or Deleteion of a nitrogen base 3. Complete the chart with the correct Amino Acid. Normal Strand of Genetic Material: mRNA AUG CCC Amino Acid Methionine (start) Mutated Strand of Genetic Material: mRNA AUG Amino Acid UUG GGC Proline Leucine Glycine CGC UUG GGC Leucine Glycine Methionine What type of mutation does this represent?Point Mutation What is the result of such a mutation?One amino acid changes 4. Complete the charts with the correct Amino Acid. Normal Strand of Genetic Material: mRNA AUG CCC UUG Amino Acid Methionine (start) Mutated Strand of Genetic Material: mRNA AUG Amino Acid Methionine GGC Proline Leucine Glycine CCC UGG GC Proline No amino acid 5. What type of mutation does this represent?frameshift 6. What is the result of such a mutation?All amino acids after the deletion or insertion will be different 7. DNA and RNA are both what type of biomolecule? Nucleic Acids 8. DNA and RNA are made of subunits called nucleotides. What are the three groups of molecules make up a nucleotide? 1. Phosphate group 2. Sugar 3. Nitrogen base 4. Use the space below to DRAW a picture of a Nucleotide P SA 9. Complete the complimentary strand or 5’ to 3’ strand of DNA. 3’ TAGCCATTACCGATC ATCGGTAATGGCTAG 5’ 10. Where does Replication occur? What is the importance of replication? DNA Replication occurs in the Nucleus and it allows the cell to make an identical copy of DNA for cell division 11. Complete the chart: DNA RNA How many strands? two One NAME the complementary Nitrogen Bases A-T C-G A-U C-G Type of sugar Deoxyribose Ribose Function Hold instructions for making proteins Carry instructions from nucleus to ribosome Nucleus From nucleus to ribosome Type location 12. Describe what occurs during Transcription.DNA is copied to make mRNA 13. Where in the cell does Transcription occur? Nucleus 14. What RNA molecule is created during transcription?mRNA 15. Transcribe the following strand of DNA(template) to create mRNA. 3’ TAGCCATTACCGATC 5’ AUCGGUAAUGGCUAG 16. A. Describe what occurs during Translation. Above picture is translation. tRNA molecules are reading the mRNA strand to create a A.A (amino acid chain) and build a protein. B. Name the molecules I, II, III, IV in the picture above. Also, what process is occurring and where is it occurring.I=tRNA Anticodon, II=mRNA III=Amino Acids IV=tRNA C. Where does Translation occur in the cell?Ribosome D. What is the end result of translation?At the ribosomes a protein is made 17. Using the following mRNA strand, what would the 3 complementary anticodons of tRNA look like and what amino acids would be attached? UGA UUC AGC ACU AAG UCG 18. Using the following DNA strand, what 3 complementary anticodons of tRNA look like and what amino acids would be attached?? TAC CCT AAG mRNA AUG GGA UUC tRNA UAC CCU AAG 19. According to Chargaffs rule, the percentage of “A” and “T” in a DNA sequence are the same. Why? Percentage of Adenine and Thymine are the same because they match together. 20. During DNA replication, a DNA molecule is split. Where is the molecule split at and what type of bond is found there?Split DNA between the nitrogen bases 21. What would happen if all the ribosomes of a cell were destroyed?Ribosomes are the protein factory and without them proteins cannot be made. 22. What part of the DNA nucleotide is responsible for the characteristics of an organism?The order of the nitrogen bases is responsible for determining the traints of an organism. 23. Using the chart, discuss why scientists believe that humans, chimps and gorillas are similar. The sequence of the Nitrogen bases is similar, which means they make similar proteins 24. Using the chart, discuss why humans, chimps and gorillas have different appearances.The slight differences in DNA create slightly different amino acids/proteins 25. What cell processes (replication, transcription, translation) directly involve DNA?Replication and transcription both use DNA. Replication is to make another DNA and transcription is to make an mRNA 26. The codon chart lists only 20 amino acids. Explain how 20 amino acids can code for many different proteins. Amino acids can be combined in many different ways, lengths and orders to create a vast array of different proteins.