* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOLOGY-DNA replication, transcription, translation (DOC 98KB)
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
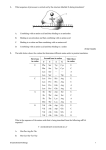
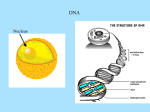
~ P A S S L e a d e r I n f o ~ DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation Questions for each group to discuss and report back to the group OR briefly discuss as a whole class before starting the activity. Why does DNA replicate? Does each new cell need DNA to be present? Where does the extra DNA come from? Does DNA replication end when the old DNA creates a completely new DNA? What is the type of replication that DNA goes through called and what does this mean? Where does translation take place? In which direction is DNA built or constructed, and why? What type of bond exists between nitrogenous bases? Are these strong or weak bonds? Building DNA double helix Materials: Pipe-Cleaners, Pegs (5 colours). Pipe-Cleaners will represent the phosphorous/ sugar back bone. The PASS facilitators will need to demonstrate this, perhaps on the board. Various colours of pegs will be used to represent the bases C, A, G and T. Students will need to explain where the sugar is joined to the nitrogenous base and the type of bonds found between them. Give the students the following code sequence to build a model: 5’ ATGTTTAAGGTGGAGCCC 3’ Replication, Transcription & Translation Using their original DNA strand made from pipe-cleaners and pegs, the students are to play out: Replication of the code Transcription from the template Translation to the Amino Acid sequence Here we need to give them the 5th colour pegs representing Uracil. Students will need to remember at which point they must use Uracil rather than Thymine. Give this to the students: 5’ ATGTTTAAGGTGGAGCCC 3’ - DNA Code Get the students to produce this: 3’ TACAAATTCCACCTCGGG 5’ -DNA template Check that the students can transcribe the correct mRNA sequence from the DNA template: 5’ AUGUUUAAGGUGGAGCCC 3’ -mRNA Check that the students can translate (using the Codon table) to the correct Amino Acid sequence: Met –Phe –Lys –Val –Glu - Pro -Amino Acid sequence Questions for Students: What is a start codon? Does all mRNA use the sequence AUG for the start codon? Second Position of Codon U F i r s t C P o s i t A i o n (5’) G U C A G UUU Phe UUC Phe UUA Leu UUG Leu UCU Ser UCC Ser UCA Ser UCG Ser UAU Tyr UAC Tyr UAA Ter UAG Ter UGU Cys UGC Cys UGA Ter UGG Trp U C A G CUU Leu CUC Leu CUA Leu CUG Leu CCU Pro CCC Pro CCA Pro CCG Pro CAU His CAC His CAA Gln CAG Gln CGU Arg CGC Arg CGA Arg CGG Arg U C A G AUU Ile AUC Ile AUA Ile AUG Met ACU Thr ACC Thr ACA Thr ACG Thr AAU Asn AAC Asn AAA Lys AAG Lys AGU Ser AGC Ser AGA Arg AGG Arg U C A G GUU Val GUC Val GUA Val GUG Val GCU Ala GCC Ala GCA Ala GCG Ala GAU Asp GAC Asp GAA Glu GAG Glu GGU Gly GGC Gly GGA Gly GGG Gly U C A G T h i r d P o s i t i o n (3’)