* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download E2 reactions
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
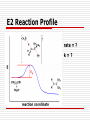
E2 Reactions E2 = elimination, bimolecular Reaction is concerted (one step) Rate = k[substrate][base] (a second order process) E2 can occur with SN2. Occurs by abstraction of H+ from a C adjacent to the C with the LG. Products follow Zaitsev’s Rule. If the base is strong, E2 will occur instead of E1 for 3° alkyl halides. E2 Reaction Mechanism One-step and requires a strong base. Best transition state is anti-coplanar. Example: t-butyl bromide + methoxide Why don’t SN2, SN1, or E1 occur? E2 Reaction Mechanism Example: t-butyl bromide + methoxide E2 Reaction Mechanism Anti-periplanar alignment allows pi bond to form from sp3 orbitals. E2 Reaction Profile rate = ? k=? Factors Affecting E2 Reactions Structure of the substrate Strength of the base Nature of the leaving group The solvent in which the reaction is run. Factors Affecting E2 Reactions Structure of the Substrate Structure of the alkyl halide: 3° > 2° >1° This is due to the stability of the more highly substituted alkene (Zaitsev’s Rule). Factors Affecting E2 Reactions Structure of the Substrate Decide whether the following substrates could react by E1 or E2 (and by SN1 or SN2). Br Cl I Br Factors Affecting E2 Reactions Strength of the Base The base must be strong. Which of the following bases favor E2 and which favor E1 reactions? H2O CH2 OH N Factors Affecting E2 Reactions the Leaving Group The LG should be good. Which of the following substrates have good LGs? Cl OCH3 H NH2 O O S O CH3 Factors Affecting E2 Reactions Solvent Effects Polarity is not so important because negative charge is spread over the transition state. Zaitsev’s Rule When two or more elimination products are possible, the more stable alkene will predominate. This is usually the product with the more substituted double bond. Zaitsev’s Rule Show the E2 elimination products that could come from: Cl Br Which E2 reaction would occur more quickly? E2 Reactions - Summary The structure of the substrate affects the rate. Relative rates for E2: 3°>2°>1°. The base must be strong. The LG should be good. The solvent should be polar. Coplanar (usually anti) transition state is required. Products will follow Zaitsev’s Rule. Can occur with SN2 for 2° alkyl halides. E2 Reactions - Summary Predict the products Cl Cl Br RO- CH3CH2OH RO- E2 Competes with SN2 for 2° Alkyl Halides E1 and E2 Reactions Base Substrate Leaving group Solvent E1 E2 weak ones work strong 3°>2° 3°>2°>1° good good polar, ionizing polar, aprotic is better E1 and E2 Reactions E1 E2 =k[RX] =k[RX][Base] Y N Stereochemistry Zaitsev’s rule Zaitsev’s rule Rearrangement ~H, ~ CH3 possible No rearrangements Rate Carbocation intermediate? How Do You Decide Which Reaction(s) Happen? The strength and structure of the nucleophile/base is paramount. Strong ones always give a second order reaction (SN2 or E2). If the base is bulky, E2 will occur instead of SN2. How Do You Decide Which Reaction(s) Happen? Now, look at the structure of the substrate. 1° alkyl halides will undergo SN2 and perhaps E2 unless rearrangement is possible. 3° alkyl halides will NOT undergo SN2. 2° alkyl halides are the toughest to predict. How Do You Decide Which Reaction(s) Happen? Evaluate, in order, Nucleophile, strength and structure -or- Base, strength and structure Structure of the alkyl halide/carbocation Leaving group Solvent YOU MUST BE ABLE TO DRAW THE MECHANISM! Elimination Reactions Predict the products Br Na+ -OCH2CH3 ethanol CH3OH OCH3 Did this product come from the reaction of 1-chlorobutane with a) sodium acetate or b) sodium t-butoxide? This product came from the reaction of 1-chlorobutane with sodium acetate. The C=O and C-O peaks show ester. O O C CH3 Did this product come from the reaction of 1-chloropentane with a) sodium acetate or b) sodium t-butoxide? This product came from the reaction of 1-chloropentane with sodium t-butoxide. The sp2C-H and C=C peaks show alkene.