* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 14antibodies
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmune encephalitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
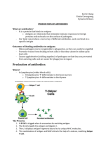
FL #14 Immune System 10BC Figure 40–8 Structure of an Antibody Section 402 Antigenbinding sites Antigen bacterium Antibody •The bacterium is an antigen An infectious disease is caused by Pathogens Bacteria, viruses, & fungi (germs). •Antibodies-protein that helps destroy pathogens Has 2 antigen binding sites Pathogen invades body Antigens on pathogen recognized by some B cells Specific Defenses A. Humoral immunity Immunity against pathogens in the body fluids (blood & lymph) 1-B cells (WBC) lymphocyte-produce antibodies 2- Antigen/antibodies Activated B cells grow and divide rapidly (a million) 3-Produce specialized B cellsplasma cells (T cells help with this also) 4-Plasma cells-release antibodies into the blood to attack the pathogen causing infection A person who receives a vaccine for the fluinfluenza Is able to produce antibodies against the flu When a person receives a vaccine(shot) their body create plasma cells (B cells) that can produce antibodies against a specific pathogen. (flu, polio, hepatitis) Function of Antibodies: Attach to antigens and attract phagocytes which engulf (eat) the antigens phagocytes-engulf & destroy bacteria –most WBC are this type “phag”=eat, “cytes”=cell Inflammatory Response Pathogens detected Millions of WBC’s produced to fight infection Blood test reveals increase in WBC’s-body is dealing w/ a serious infection Immune system releases chemicals that increase core temperature FEVER- INCREASED body temp Many pathogens survive in a narrow temp. range Elevated temp:1) slows down or stops growth of pathogens 2) increase heart rate, WBC’s get to infection quicker 3)Speeds activities of WBC’s & rate of chemical reactions that repair damaged tissues 1. (10b) Humoral immunity is carried out by A.Killer T Cells B.Lymphocytes C.Antibodies D.macrophages 2. (10b) In the figure below the red bacterium represents a A.Antigen or pathogen B.Antibody C.Killer T Cell D.Antigen binding site E 3. (10b) Which of the following is the function of antibodies in the immune response? A.Antibodies produce antibiotics. B.Antibodies attach to antigens and attract phagocytes which engulf & destroy the antigen. C.Antibodies produce interferon. 4. (10c) When a person receives a vaccine, his or her body creates a memory that A.Receives antibodies against a specific pathogen B.Creates plasma cells that can produce antibodies against that specific pathogen. C.Has polio antibodies in the blood D.Has antipolio killer T cells in blood 5. 10B Antibodies fight infections by A. Preventing Viruses from replicating B. Killing infected cells C. Helping leucocytes identify pathogens D. Growing green mold that stops bacterial growth