* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune Response
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
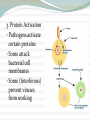
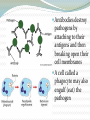
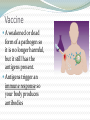
Non – Specific Immune Response A pathogen gets inside and your body responds by trying to kill/inhibit the pathogen Three basic responses: 1. Fever – high temps destroy pathogens 2. Inflammation (swelling) Skin/cells are damaged, pathogens enter Cells recognize invaders and release chemicals called histamines These cause increased blood flow (which causes swelling) to get more white blood cells WBCs attack pathogens Lymph nodes may also swell with fluid when they fight infection 3. Protein Activation Pathogens activate certain proteins Some attack bacterial cell membranes Some (Interferons) prevent viruses from working Specific Immune Response Pathogens have specific proteins that act as name tags – it lets the the body know they’re foreign A substance on the pathogen called an antigen causes the body to respond The response is to release WBC’s & produce antibodies Antibodies destroy pathogens by attaching to their antigens and then breaking open their cell membranes A cell called a phagocyte may also engulf (eat) the pathogen Immunity The ability of the body to resist certain diseases for the long term – 2 types Active Immunity – body makes its own antibodies - occurs if you had the disease or got vaccinated Passive Immunity – temporary immunity by receiving antibodies Ex: Mother to child through breast milk Vaccine A weakened or dead form of a pathogen so it is no longer harmful, but it still has the antigens present. Antigens trigger an immune response so your body produces antibodies Can you… List and explain the three non-specific immune responses? Explain what an antigen is? Explain the relationship between an antigen and an antibody? Explain how and why a vaccine works?