* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Behavioral therapy
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social Bonding and Nurture Kinship wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Social perception wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
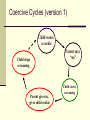
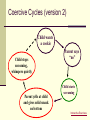
Behavioral Psychotherapy Learning the A-B-Cs Defining Behavior What we do…Outward manifestation of our inner selves Communication (to others) of how we feel and think and who we are Tool we use to accomplish goals, but…may also prevent us from reaching goals Behaviorist Manifesto Psychology as the behaviorist views it is a purely objective experimental branch of natural science. Its theoretical goal is the prediction and control of behavior. Introspection forms no essential part of its methods, nor is the scientific value of its data dependent upon the readiness with which they lend themselves to interpretation in terms of consciousness. The behaviorist, in his efforts to get a unitary scheme of animal response, recognizes no dividing line between man and brute. The behavior of man, with all of its refinement and complexity, forms only a part of the behaviorist's total scheme of investigation (Watson, 1913). History Two historical events are foundations for BT Experimental research on animal learning Ivan Pavlov’s classical conditioning Aversion therapy Systematic desensitization Flooding E.L. Thorndike’s research on the influence of consequences 1905: Law of effect blank slate “Responses that produce a satisfying effect in a particular situation become more likely to occur again in that situation, and responses that produce a discomforting effect become less likely to occur again in that situation.” Behavior management /modification (using token economies) Behavior and response prevention (Tx for OCD) History (continued) Rise of behaviorism in the 1900s John Watson’s emphasis on environmental events Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in and I'll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select – doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief and, yes, even beggar-man and thief, regardless of his talents, penchants, tendencies, abilities, vocations, and race of his ancestors. I am going beyond my facts and I admit it, but so have the advocates of the contrary and they have been doing it for many thousands of years. (Watson, 1930) Letter from Skinner’s daughter B.F. Skinner’s radical behaviorism: Operant conditioning explains all History (continued) “Little Albert” experiment Watson forced out of psychology in 1920 (Rosalie Rayner, Mary Ickes, Harold Ickes) Formal beginnings of BT were in the 1950s, primarily with children By the 1970s, emphasis shifted to social learning theory & cognition The 1980s and 1990s showed increased attention to affect Currently, 14% of clinical faculty are “behaviorists” while 42% emphasize cognitive-behavioral or social learning approaches Basic Concepts Three main approaches Applied Behavior analysis (the focus today!) Mediational Stimulus-Response (S-R) model Based on Skinner’s radical behaviorism Behavior is considered to be a function of its consequences Cognitions are considered private events and not proper subjects for scientific study Makes use of reinforcement, punishment, and other operant conditioning principles Private events, including thoughts and feelings are integral Examples include systematic sensitization and flooding Social-cognitive theory Person is his/her own agent of change It is not the experience, but person’s interpretation of the experience Common characteristics 1. Commitment to consistent empirically determined theory 2. Abnormal behaviors are nonpathological “problems of living” 3. Abnormal behavior assumed to be acquired and maintained in the same manner as normal behavior 4. Behavior assessment focuses on current determinants rather than on the analysis of possible historical antecedents 5. Rooted in the notion of mutual influences: Parents effect children, but children also effect parents 6. Specificity is vital. Person is best understood by what he/she does in a particular situation 7. Treatment is individually tailored to different problems in different individuals 8. Understanding origins of problem NOT essential for producing change Process of psychotherapy Considerations for starting treatment Must identify specific problem (jointly with client or parents) Does the problem require treatment What will happen if nothing is done What treatment is likely to be most effective Who is the best person to deliver the treatment (e.g., therapist, parents, teachers) deficit behavior excessive behavior Someone present in environment is better Someone capable and willing to implement plan What is the best context for treatment (e.g., school, home) Do a thorough assessment (e.g., identify discriminant stimuli for problematic behavior) Process of psychotherapy (treatment) Design an appropriate treatment plan using positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, and punishment techniques Figure out the most appropriate reinforcers a. Resistant to saturation (M&Ms are bad, what’s better?) b. Able to be administered in small units (trip to Florida?) c. Able to be administered immediately following behavior d. Must be in control of agent (e.g., not dependent on weather) e. Must be compatible with treatment plan f. Must be practical g. Conditioned reinforcers work well (token reinforcers that are associated with other positive reinforcers (points, tokens) Establish reinforcement schedule, based on behavior frequency a. Low frequency = continuous reinforcement b. High frequency = fixed interval, fixed ratio, or variable ratio Treatment (cont.) Break behavior into components and use shaping techniques Reward approximations (homework example) Know the assignment Bring homework materials home Go to study area without prompt Remain in study area on task Get the work done Turn in the assignment Use prompting and modeling Have a contingency contract (an agreement about what is expected and the consequences of not doing it) Treatment (for unwanted behaviors) For unwanted behaviors Extinguish by removing reinforcers that used to follow the unwanted behavior Give reinforcers for a competing behavior If punishment is used, it should follow these rules As intense as possible (start with maximum intensity) As frequent as possible As immediate as possible Relatively brief Can’t be a way out of doing something Can’t associate w/ positive reinforcers (don’t apologize) Applied Behavioral Analysis: Central Constructs Client-counselor relationship is imperative and counselors exhibit high levels of empathy, self-congruence and interpersonal contact. The relationship is collaborative and relationship variables differ according to client and culture. Operationalization of Behavior: Focuses on the concreteness and specifics of behavior. Vagueness is transformed into objective, observable actions. Functional Analysis: The ABC’s of behavior. An individual's behavior is directly related to events and stimuli in the environment. Reinforcement: Behavior develops and maintains itself through a system of punishments and rewards. Goals: These are designed to make specific behavioral changes. concrete, specific, observable and measurable meet biological and social needs; adaptive avoid pain and discomfort ” Coercive Cycles (version 1) Child wants a cookie Child stops screaming Parent gives in, gives child cookie Parent says “no” Child starts screaming Coercive Cycles (version 2) Child wants a cookie Child stops screaming, whimpers quietly Parent says “no” Child starts screaming Parent yells at child and gives solid smack on bottom Interactive Exercises Behavioral Methods Operant Conditioning (Applied Behavior Analysis) Relaxation Training (demo) Systematic Desensitization Flooding Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) Social Skills Training Mindfulness, Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)