* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Extra Membrane Ideas P.P - SchoolWorld an Edline Solution
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
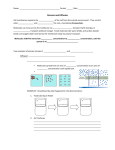
Extra Membrane Ideas I. Osmosis • *** Selectively Permeable*** - membranes that only allow ______________ things through. For example, a membrane might allow little things like _______________ to ___________ through it but not have holes that allow larger things like ___________ or ________________ to pass through. • Selectively permeable membranes make it so that particles like salt _________ diffuse from a _________________ to a __________________ salt concentration. So, how can balance in concentration be created? *** _______________*** - the______________ of ______________ from a _________________ water concentration to a _________________ water concentration through a __________________ __________________ membrane. Water will move in the direction where there is a ________ concentration of salt (and hence a _______ concentration of water). II. Osmosis and the Cell Membrane The cell ___________________ is selectively _______________, water moves freely across the cell's membrane, by diffusion. A simple rule to remember is: Salt Sucks Salt - When it is concentrated inside or outside the cell, it will draw the water in its direction. This is also why you get thirsty after eating something salty. ______________________ Solution - When the concentration of solute (salt) is _______ ___________ on both sides of the cell membrane, the water will move back in forth but it won't have any result on the overall amount of water on either side. "ISO" means the ____________ ______________________ Solution - There are _________solute (salt) molecules outside the cell. That means that there is _______ water ___________ the cell and it will diffuse _____________ (osmosis). (Since “salt sucks,” water will move _______ the cell.) The cell will __________ water and grow _________. In plant cells, the central vacuoles will fill and the plant becomes stiff and rigid, the cell wall keeps the plant from bursting. In animal cells, the cell may be in danger of_____________. "HYPO" means _______ ______________________ Solution - There are ________ solute (salt) molecules outside the cell. That means that there is ________ water __________ the cell and it will diffuse _____________ (osmosis). (Since “salt sucks,” water will move __________ ____ the cell.) In plant cells, the central vacuole loses water and the cells shrink, causing ___________ . In animal cells, the cells also ___________. In both cases, the cell may _______. "HYPER" means ___________ • How could we revive the lettuce? • Why is salt used for curing meat? • What must be considered when giving injections to patients at hospital? Which word applies to each: hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic? Which word applies to each: hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic? III. Moving Massive Pieces of Food and Other Material (chunks) Through Membrane (for globs that are way too big… even for protein channels) _____________ : ______________: http://www.yellowtang.org/animations/endoc ytosis_exocytosis.swf __________________: _________________: Good pics of exocytosis