* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt file
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Process tracing wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Visual extinction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Visual servoing wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
C1 and P1 (neuroscience) wikipedia , lookup
Inferior temporal gyrus wikipedia , lookup
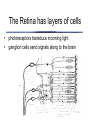
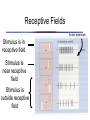
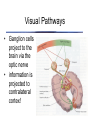
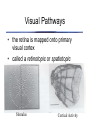
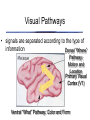
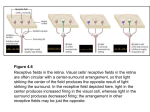
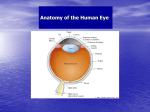
The Retina has layers of cells • • photoreceptors transduce incoming light ganglion cells send signals along to the brain Two kinds of Photoreceptors • 2 types of photoreceptors: rods and cones • rods are very sensitive - useful in dim light • The Retina • Rods and cones are distributed differently across the retina The Retina • visual acuity (ability to see detail) depends on cones - thus acuity varies across the visual field The Retina • Why don’t you notice your blind spot? The Retina • Why don’t you notice your blind spot? – Blindspots don’t overlap! – Your brain “fills in” the missing information – The specific information in the blindspot isn’t much more missing than the rest of the periphery! The Retina • • three types of cones: short, medium, and long different absorptions enable color vision Neurons “collect” information • each ganglion cell integrates information from a particular spot on the retina called its receptive field Receptive Fields Action potentials Stimulus is in receptive field Stimulus is near receptive field Stimulus is outside receptive field Visual Pathways • Ganglion cells project to the brain via the optic nerve • information is projected to contralateral cortex! Visual Pathways • the retina is mapped onto primary visual cortex • called a retinotopic or spatiotopic map Stimulus Cortical Activity Visual Pathways • signals are separated according to the type of information Dorsal “Where” Pathway: Motion and Location Primary Visual Cortex (V1) Ventral “What” Pathway: Color and Form Seeing Seeing • Discussion of Gregory’s Article on Visual Illusions - Tuesday Oct 23 Seeing • Seeing is the process of converting electromagnetic radiation into a conscious mental event Seeing • visual system faces many challenges – – – – too much information too little information conflicting information ambiguous information Seeing • too much information Seeing • too little information Seeing • Conflicting Information Seeing • Ambiguous information Seeing • We will consider two aspects of vision to explore how the brain overcomes these challenges: – Seeing depth – Seeing in color