* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate Variability, Climate Change
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Snowball Earth wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
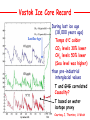
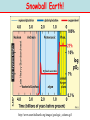
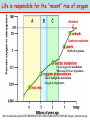
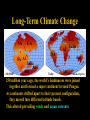
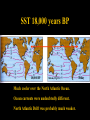
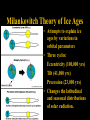
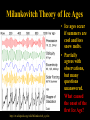
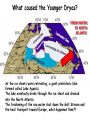
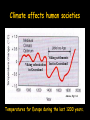
NATS 101 Lecture QuickTime™ and a decompressor Variability Natural Climate are needed to see this picture. Artist’s rendition of snowball earth, 650 Mya Perspective: Time Scales 4.6 Gya 2.1 Gya 13.7 Gya 3.5 Gya 65 Mya 21 s Avg. human life span=0.15 s http://ocw.mit.edu/OcwWeb/Earth--Atmospheric--and-Planetary-Sciences/12-301Fall-2006/LectureNotes/index.htm Perspective: Astronomic Space Scales 13.7 Ga (+/- 1%) 1 ly = 1016 m ly=light year http://ocw.mit.edu/OcwWeb/Earth--Atmospheric--and-Planetary-Sciences/12-301Fall-2006/LectureNotes/index.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Earth What is Climate Change? • Climate change - A significant shift in the mean state and event frequency of the atmosphere. • Climate change is a normal component of the Earth’s natural variability. • Climate change occurs on all time and space scales. • We know that “a plethora of evidence exists that indicates the climate of the Earth has changed.” What is that evidence? How do we know what we know? Causes of Climate Change Astronomical Composition Surface Detecting Change With Proxies Scientifically, the best way to detect change is to directly measure it. Data available last 100-200 yrs. Unfortunately for the timescales of interest in climate science, we were not always able (interested in?) to measure quantities such as temperature, precipitation, wind speed, direction, greenhouse gas levels, etc. But, obviously we want to know what these properties were and how they changed in the past to test our understanding of how climate changes. The study of past climate is known as paleoclimate science. Courtesy J. Thornton, U Wash Detecting Change With Proxies Another property/qty that is a function of property of interest. Think approximate The measured property is a PROXY for the one of interest. Courtesy J. Thornton, U Wash Unlocking “Stored” Climate Change • Modern Instrument Record • Tree Rings • Ice Cores • Sediment cores • Rock formations/types Record: 1000 ~ Present day “Length” of growing season Good versus stressed years Major fires Courtesy J. Thornton, U Wash Unlocking “Stored” Climate Change • Modern Instrument Record • Tree Rings • Ice Cores • Sediment cores • Rock formations/types Record: ~ 1Mya to 20th cent Inert gases (CO2, CH4, N2O,…) Particulates (soot, ash, etc) Temperature?? Courtesy J. Thornton, U Wash Unlocking “Stored” Climate Change • Modern Instrument Record • Tree Rings • Ice Cores • Sediment cores • Rock formations/types Courtesy J. Thornton, U Wash Record: ~ 200 Mya Microfossils (ocean T), Volcanic glass Organic detritus Magnetic pole location Unlocking “Stored” Climate Change • Modern Instrument Record • Tree Rings • Ice Cores • Sediment Cores • Rock formations/types Banded Iron Formations BIFs tied up oceanic O2 Prevented atmospheric O2 Date no later than ~2 GYA Record: ~ 4.5 Gya Geologic formation Geochemical analysis Magnetic pole Continental Location Fossil record Water Cycle – Water Isotope T Proxy 18O/16O 18O/16O 18O/16O lower 18O/16O lower still low high Courtesy J. Thornton, U Wash Vostok Ice Core Record Last Ice Age During last ice age (18,000 years ago) Temps 6oC colder CO2 levels 30% lower CH4 levels 50% lower (Sea level was higher) than pre-industrial interglacial values T and GHG correlated Causality? T based on water isotope proxy Courtesy J. Thornton, U Wash O18 analysis of ocean sediments can be used to construct past temperatures Cold Warm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%CE%9418O 600 Million Years of Climate The past climate of the Earth can be deduced “by mapping the distribution of ancient coals, desert deposits, tropical soils, salt deposits, glacial material, as well as the distribution of plants and animals that are sensitive to climate, such as alligators, palm trees & mangrove swamps.” 1.8 Mya 65 Mya 145 Mya 200 Mya 251 Mya 299 Mya 359 Mya 417 Mya 444 Mya 490 Mya 542 Mya http://www.scotese.com/climate.htm 540 Mya of Climate Change from O18 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxygen_isotope_ratio_cycle Snowball Earth! http://www.snowballearth.org/images/geologic_column.gif Snowball Earth: Some Evidence cap carbonates dropstones http://www-eps.harvard.edu/people/faculty/hoffman/Snowball-fig11.jpg Basic physics are understood: Runaway ice-albedo feedback http://nai.nasa.gov/newsletter/03182005/snowball.jpg How does earth thaw? CO2? Life is responsible for the “recent” rise of oxygen Cambrian explosion Multicell organisms Use of oxygen for metabolism. Water and CO2 are byproducts. Use of sunlight for metabolism. Oxygen is a byproduct. http://si.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E0%B6%BB%E0%B7%96%E0%B6%B4%E0%B6%BA:Oxygen_atmosphere.png Atmospheric constituents have changed radically through the ages Dimmer Sun Brighter Sun http://www.ozh2o.com/atmos.jpg Long-Term Climate Change NA E-A SA Af 180 M BP India Aus Ant NA E-A Af India SA Today Aus Ant Ahrens, Fig 13.6 250 million years ago, the world’s landmasses were joined together and formed a super continent termed Pangea. As continents drifted apart to their present configuration, they moved into different latitude bands. This altered prevailing winds and ocean currents. Long-Term Climate Change • Circumpolar ocean current formed around Antarctica 40-55 MY ago as Antarctica and Australia separated. • Kept warm air from low latitudes from reaching into Antarctica. • Absence of warm air accelerated growth of the Antarctic ice sheet. http://www.ace.mmu.ac.uk/eae/Climate_Change/Older/Continental_Drift.html Most Recent Ice Age Aguado and Burt, Fig 16-4 Extend of continental glaciers 18,000 years BP. Sea level was 100-125 m lower than present. Bering land bridge between Siberia and Alaska. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Recent_Sea_Level_Rise.png SST 18,000 years BP 18,000 BP Ahrens, Fig 13.2 Much cooler over the North Atlantic Ocean. Ocean currents were undoubtedly different. North Atlantic Drift was probably much weaker. Today Milankovitch Theory of Ice Ages • Attempts to explain ice ages by variations in orbital parameters • Three cycles: Eccentricity (100,000 yrs) Tilt (41,000 yrs) Precession (23,000 yrs) • Changes the latitudinal and seasonal distributions of solar radiation. Milankovitch Theory Change in daily solar radiation at top of atmosphere at June solstice Changes as large as ~15% occur Milankovitch Theory of Ice Ages • Ice ages occur if summers are cool and less snow melts. • Partially agrees with observations, but many questions unanswered. What caused the onset of the first Ice Age? http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Milankovitch_cycles Temperatures since the last Ice Age… the time that humans have flourished Glacial advance Glacial retreat Apline advance Rapid melt Ahrens, Fig 13.3 Younger-Dryas Rapid cooling at the start occurred over a period of 1,000 yrs. The abrupt warming at the end occurred in only a few yrs! What caused the Younger Dryas? FRESH WATER TO NORTH ATLANTIC As the ice sheets were retreating, a giant prehistoric lake formed called Lake Agassiz. The lake eventually broke through the ice sheet and drained into the North Atlantic. The freshening of the sea water shut down the Gulf Stream and the heat transport toward Europe, what happened then?? Climate affects human societies Viking colonization in Greenland Viking settlements lost in Greenland Ahrens, Fig 13.4 Temperatures for Europe during the last 1200 years. Evidence of Climate Change 0.6oC warming past century Anthropogenic warming? Ahrens, Fig 13.5 Surface temperatures based on meteorological observations. Is the warming of the past century due to human activities? Complexity of Climate System The climate system involves numerous, interrelated components Feedback Mechanisms Examples of feedbacks in the climate system with global warming Positive feedback = Enhances the warming Negative feedback = Mitigates the warming IF YOU HAVE THE FOLLOWING: MORE WATER VAPOR: Positive feedback because it’s a greenhouse gas. LESS SEA ICE: Positive feedback because more solar radiation is absorbed instead of reflected. MORE CLOUDS: Feedback can be positive or negative depending on the type of clouds. THIS IS STILL A BIG UNKNOWN… HiGH CLOUDS: Positive feedback LOW CLOUDS: Negative feedback MORE AEROSOLS: Negative feedback because more solar radiation is reflected. Key Points: Climate Change • Proxy data are used to infer the past climate. • Data show that the Earth’s Climate Has changed in the past Is changing now And will continue to change • There has been 1F warming during the past century, half of which has occurred during the past 30 years. Key Points: Climate Change • The climate system is very complex. Contains hundreds of feedback mechanisms. Feedbacks are not completely understood. Biosphere-Atmosphere interactions. Key Points: Climate Change • • • Three general climate change mechanisms: 1) Astronomical 2) Atmospheric composition 3) Earth’s surface Humans modifying 2 and 3 on global scale. Are recent climate and weather changes due to natural causes or human activities? Next Time Assignment for Next Lecture Anthropogenic Climate Change • Reading- Ahrens 4th: 373-399 5th: 383-409 • Homework11- D2L 4th-Pg. 399: 14.12, 15, 16, 19 5th-Pg. 412: 14.12, 15, 16, 19 Do Not Submit D2L