* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climatic changes in the last 200 years
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Urban heat island wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
North Report wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Solar activity and climate wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
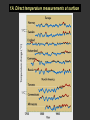
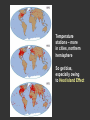
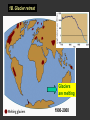
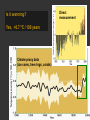
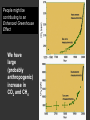
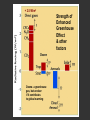
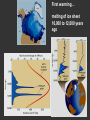
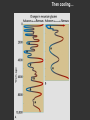
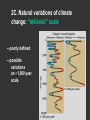
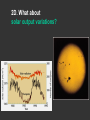
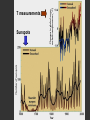
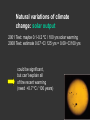
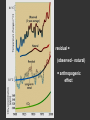
Climatic changes in the last 200 years (Ch. 17 & 18) 1. Is it warming? --climate proxy info (recap) -- info from historical & instrumental records 2. What does it mean? 1. Is it warming? Climate proxy info recap (ice cores, tree rings, corals) Average northern hemisphere surface temperatures Long-term gradual T decrease 1900s unusually warm Late 1400s & 1600s unusually cold 1940-1970 cool period within warmer century Is it warming? Info from historical & instrumental records A. direct T measurements B. glacier advances & retreats C. sea level D. cloud cover E. snow & ice cover 1A. Direct temperature measurements at surface Temperature stations – more in cities, northern hemisphere So get bias, especially owing to Heat Island Effect What is the Urban Heat Island Effect? What is the Urban Heat Island Effect? -- cities have low albedo (e.g. asphalt), should absorb more solar radiation -- most temperature stations located in urban areas -- this could bias temperature data -- satellite data earlier said to disagree with ground measurements, but satellite data have their own problems -- have to correct for biases Subsurface temperatures -- Land -- measure T in boreholes, 10s of m deep -- hundreds of stations on all continents -- records extend over last 100 years -- complicated by snow, forests -- T up on all continents, by ~0.3-0.8 oC Borehole ground temperatures Borehole locations > Models, > based on borehole data (T up ~0.3-0.8 oC) Subsurface temperatures -- Ocean -- measure T in uppermost 3 km -- below wind mixing zone of 100 m -- records extend over last 50 years -- T up in oceans, by ~0.06 oC -- seems small, but recall large heat capacity of water (translates to a lot of energy stored in oceans– more than in atmosphere) Shallow ocean warming Up 0.06 oC 1A. Global average surface temperature based on direct measurements-corrects for urban heat island effect +0.3 Overall T increase last 100 years -0.3 Linear approx: +0.6 oC/100 years Best estimate: +0.7 oC/100 years 1B. Glacier retreat Glaciers are melting 1900-2000 1C. Two estimates of global sea level • Takes into account bedrock movement & water impoundment in dams • Rise caused by melting ice & thermal expansion of ocean 15 cm rise in last 100 years 1D. Cloud cover in two areas We see more cloudiness More evaporation from surface? More seed particles in air? Cooler at high-altitude? (Colder air can’t hold as much water before condensation occurs) 1E. Snow cover Since 1980 we see gradually less arctic snow cover Northern hemisphere 1E. Arctic sea ice cover Since 1970 we see 6% less area of Arctic sea ice Sea ice has also thinned from 3 to 2 m (40% decrease) Historical & instrumental climate data: conclusions for last 100 years ____________________________________ 1. Have good evidence for overall warming 2. Evidence: direct T increase retreat of glaciers rise of sea level less arctic snow & ice 3. It seems to be more cloudy -- probably result of more surface evaporation 4. Direct T measurements imply avg. +0.7 oC/100 year Is it warming? Yes, +0.7 oC / 100 years Cimate proxy data (ice cores, tree rings, corals) Direct measurement 2. What does recent warming mean? It depends… Can we attribute all of the warming to an anthropogenic effect? People might be contributing to an Enhanced Greenhouse Effect We have large (probably anthropogenic) increase in CO2 and CH4 estimate 2.5 / 150 = 0.017 ~1.7% increase in strength of greenhouse effect Direct addition of greenhouse gases by people + 2.5 W/m2 Strength of Enhanced Greenhouse Effect & other factors Ozone- a greenhouse gas, but unclear if it contributes to global warming Greenhouse debate Are people causing climate change? Probably some. How much warming is natural, how much anthropogenic? Uncertain! 2. What does recent warming mean? Consider natural variations of climate change: recent trends A. tectonic scale B. orbital scale C. millenial D. what about solar output variations? 2A. Natural variations of climate change: tectonic scale Greenhouse world: 100 m.y. ago Leaf outline data: ~10 oC cooling in last 50 m.y. O-isotope data, deep oceans: ~13 oC cooling in last 50 m.y. Natural variations of climate change: tectonic scale -10 oC / 50 m.y. = -0.000002 oC / 100 years not important for this century (infer +0.7 oC / 100 years) 2B. Natural variations of climate change: orbital scale 41,000 year cycle (obliquity) 23,000 year cycle First warming… melting of ice sheet 16,000 to 12,000 years ago Then cooling… Synthesis of studies using climate proxies (ice cores, tree rings, corals) Average northern hemisphere surface temperatures Long-term gradual T decrease: 0.2 oC/1000 yrs Orbital cooling Natural variations of climate change: orbital scale -0.2 oC / 1000 yrs = -0.02 oC / 100 years Overall effect small (need +0.7 oC / 100 years) 2C. Natural variations of climate change: “millenial” scale -- poorly defined -- possible variations on ~1,000 year scale Natural variations of climate change: millenial scale Perhaps + or -0.2 oC / 1000 yrs = + or -0.02 oC / 100 years overall effect small (need +0.7 oC / 100 years) 2D. What about solar output variations? T measurements Sunspots Natural variations of climate change: solar output 2001 Text: maybe 0.1-0.2 oC / 100 yrs solar warming 2008 Text: estimate 0.07 oC/ 125 yrs = 0.09 oC/100 yrs could be significant, but can’t explain all of the recent warming (need +0.7 oC / 100 years) Infer: +0.7 oC/100 yr An important role for solar forcing? “Some scientists argue that solar forcing explains much of the observed temperature variations in the 20th Century… The problem with this argument is that it demands strong feedbacks within the climate system to make Earth highly sensitive to small changes in the Sun’s strength, yet it has to deny the strong action of these same feedbacks… to changes in the concentration of greenhouse gases”. An important role for solar forcing? “A more consistent interpretation is that the climate responds with similar sensitivity both to solar forcing and to changes in greenhouse gases, both of which have played roles in temperature changes during the Twentienth Century.” So what about solar output variations? GCM models: +0.06 oC / 100 yrs to +0.3 oC / 100 yrs inferred: 0.7 oC / 100 yrs residual = (observed - natural) = anthropogenic effect