* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download S, L = global average values of incoming solar & outgoing
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
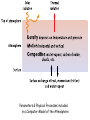
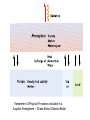
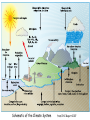
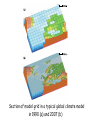
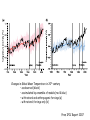
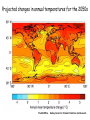
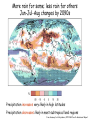
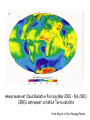
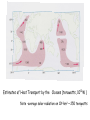
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C3W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized • Weather Forecasting and Research • Climate Prediction and Research Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System Identifies: • starting conditions for weather or climate Integrates: • the dynamical equations of motion • the physical equations of state, energy etc • algorithms describing all relevant processes NOT based on empirical or statistical information Parameters & Physical Processes included in a Computer Model of the Atmosphere Horizontal Grids for Global and Regional Models UK Met Office jp05 Weather shows large variability in space and time Detailed weather forecasting only possible 10 to 30 days ahead Climate (= average weather) also shows large variability Is forecasting of human influence on climate a possibility? Components of the Climate System • • • • • Atmosphere Oceans Cryosphere Land Surface Biosphere All these components interact closely Parameters & Physical Processes included in a Coupled Atmosphere – Ocean Global Climate Model Schematic of the Climate System from IPCC Report 2007 Computer Modeling of the Climate an essential tool that provides the means to add together all the non-linear processes and effects including positive & negative feedbacks Essential for estimating future climate Section of model grid in a typical global climate model in 1990 (a) and 2007 (b) Climate (= average weather) shows large variability from month to month, year to year Global Climate (= patterns of climate averaged over globe) shows clear response to external forcing factors, e.g. • Changes in Solar Radiation • Volcanoes • Greenhouse gases Predicted & Observed changes in Global Average Temperature after the eruption of Mount Pinatubo in 1991 from IPCC Report 1996 Changes in Global Mean Temperature in 20th century • as observed (black) • as simulated by ensemble of models (red & blue) – with natural and anthropogenic forcings (a) - with natural forcings only (b) From IPCC Report 2007 Patterns of Chaos LORENZ ATTRACTOR A solution of set of three coupled differential equations, dx/dt = σ (y - x), dy/dt = x (ρ - z) - y, dz/dt = x y - β z, that arise in studies of atmospheric convection Lorenz Attractor distorted by External Forcing (after Palmer 1999) Future Climate under increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions The enhanced greenhouse effect with doubled CO2 S, L = global average values of incoming solar & outgoing long wave radiation at top of atmosphere Some main impacts of climate change • More intense heat waves • Sea level rise • More intense hydrological cycle jp14 Projected changes in annual temperatures for the 2050s The MetOffice. Hadley Center for Climate Prediction and Research. More rain for some; less rain for others Jun-Jul-Aug changes by 2090s Precipitation increases very likely in high latitudes Precipitation decreases likely in most subtropical land regions From Summary for Policymakers, IPCC WG1 Fourth Assessment Report Increased global average surface temperature leads on average to: • More evaporation of water vapour from oceans • More water vapour in atmosphere • More average precipitation (as now observed) • More latent heat release into atmosphere* • More intense hydrological cycle • Increase in risk of floods and droughts * from condensation of water vapour - a large source of energy Proportion of land surface in drought - 3 computer simulations under A2 Emissions Scenario (after E Burke et al, Hadley Centre) Proportion of land under extreme drought (from Burke 2006) • 1980 ~ 1% • 2005 ~ 3% • 2040 (+2 deg) ~ 8% • 2070 (+3 deg) ~ 18% Some Feedbacks in the Climate System • Water-vapour feedback • Cloud – Radiation feedback • Ocean Circulation Feedback • • Ice – Albedo feedback • CO2 fertilization effect • Climate/carbon-cycle feedback Cloud -Radiation Feedback largest contributor to uncertainty in climate sensitivity to increase in greenhouse gases Physical Processes associated with Clouds lead to feedbacks both +ve (high clouds) & -ve (low clouds) Clouds influence average temperature + 3% High Clouds + 0.3º + 3% Low Clouds – 1.0º Polluted clouds have smaller particles - leading to • more reflection of sunlight from the cloud top, • less radiation at the surface, • less precipitation & • longer cloud lifetime Annual mean net Cloud Radiative Forcing (Mar 2000 - Feb 2001) CERES instrument on NASA Terra satellite from King et al Our Changing Planet Ocean circulation feedback Estimates of Heat Transport by the Oceans (terawatts, 1012W ) Note -average solar radiation on 106 km2 ~ 250 terawatts , How can models be validated? • Comparison with Recent Climate • Comparison with Past Climates • Comparison with particular events Sources of Climate Data Instruments, in-situ, passive & active remote sensing, mounted on satellites, aircraft, balloons, ships, buoys, land surface etc Envisat - 2002 Nimbus - 1970s jp02 Instruments on ESA’s Earth Observation Satellite, ENVISAT Passive Active • • • • • • • RA-2 • ASAR • DORIS AATSR MIPAS MERIS SCIAMACHY MWR GOMOS Illustrating Data Overload Examples of Climate Modeling Research Projects • How well can models describe extreme weather? • How well can models forecast extreme climate events e.g. floods, droughts, storms etc – timing & location? • Cloud- Radiation Feedback What is its average sign & size of how do they vary? • How well do models describe Ocean-Circulation Feedback on Climate? • What are the influences of particles (aerosols) on climate? • What is the relative influence of different greenhouse gases? • How can human communities adapt to climate change? • What model improvements could best help mitigation policy? • What can we learn from past climates? • How can models represent sub-grid-scale motions more accurately? Possible Collaborations for C3W in Climate Modeling • with Met Office • with European partners • etc