* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11a - Genetic Mutation Notes
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
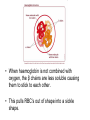
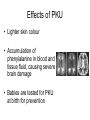
Genetic Mutations Mutation: An unpredictable change in the genetic material of an organism Gene Mutation: A change in the structure of a DNA molecule, producing a different allele of a gene Chromosome Mutation: A change in the entire structure or number of whole chromosomes Causes of Mutations Mutations occur randomly with no obvious cause. Mutagens: Substances that increase the chances of mutation occurring Ex: Ionizing Radiation, Ultraviolet Radiation, Smoking, UV light Types of Mutations • Base Substitution – One nucleotide base takes the place of another • One amino acid is changed in the sequence Types of Mutations • Base Addition – One or more extra nucleotide bases added to a sequence • Base Deletion – One or more nucleotide bases are lost from the sequence • Incorrect sequence of amino acids • Incorrect sequence of amino acids • Frame Shift Mutations Which types of mutations have the greatest impacts? Silent mutations – Mutation that has no apparent effect on an organism Sickle Cell Anemia Sickle Cell Anemia • Base substitution with a significant side effect on phenotype • The affected gene codes for the oxygen carrying pigment HAEMOGLOBIN. Normal Amino Acid Sequence: Val-His-Leu-Thr-Pro-Glu-Glu-LysSickle Cell Anemia Sequence: Val-His-Leu-Thr-Pro-Val-Glu-Lys- • When haemoglobin is not combined with oxygen, the β chains are less soluble causing them to stick to each other. • This pulls RBC’s out of shape into a sickle shape. Phenylketonuria (PKU) • Base substitution • The affected gene codes for an enzyme (phenylalanine hydroxylase), which is not present in people with the mutation • This enzyme helps catalyse the conversion of phenylalanine to triosine, which is then converted to melanine Effects of PKU • Lighter skin colour • Accumulation of phenylalanine in blood and tissue fluid, causing severe brain damage • Babies are tested for PKU at birth for prevention