* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Heredity
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
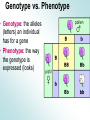
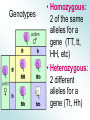
GENETICS Basic Heredity A study of gene inheritance from one generation to the next. History of Heredity • Gregor Mendel is father of modern genetics • Mendel used pea plants to examine heredity from one generation to the next Mendel’s Laws • 1) Law of Segregation • There are two factors controlling each trait • These factors are “alleles” • The alleles separate so that gametes only get 1 of the two alleles • 2) Rule of Dominance • One allele is always dominant over the other • 3) Law of Independent Assortment Genetics Rules • Dominant alleles are written with CAPITAL letters • Having 1 dominant alleles means the trait will be expressed • Recessive alleles are written with lowercase • Must have 2 recessive alleles for the trait to be expressed Genotype vs. Phenotype • Genotype: the alleles (letters) an individual has for a gene • Phenotype: the way the genotype is expressed (looks) Geno or Pheno? • Tt • HH • Red hair • BB • Blue eyes Genotypes • Homozygous: 2 of the same alleles for a gene (TT, tt, HH, etc) • Heterozygous: 2 different alleles for a gene (Tt, Hh) Hetero or Homo? • BB • Bb • Hh • tt • dD