* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
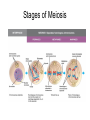
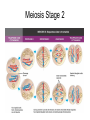
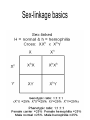
Meiosis/Genetics Topic 4 Stages of Meiosis Meiosis Stage 2 Genes and Chromosomes • Terminology: • Genotype – genetic constitution of a gene/org • Phenotype – physical expression of a gene • Dominant allele – form of the gene that is expressed even when only 1 is present • Recessive allele – form of the gene that is only expressed when both alleles are recessive Terminology cont’d • Codominant allele – when two two forms of a gene are both expressed when paired together • Locus – the location of a gene/allele on a chromosome • Homozygous – when both alleles of a gene are the same (ex. aa, AA) • Heterozygous – when both alleles of a gene Terminology cont’d • Carrier – an individual of heterozygous makeup that carriers, and therefore can pass on, a disease causing allele but doesn’t express that trait • Test cross – when an individual of known phenotype but unknown genotype (AA or Aa) is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual in order to determine its genetic make-up. Mendelian Genetics – Monohybrid Cross Classical Punett's Square is a way to determine ways traits can segregate parental P cross a a A Aa Aa F1 cross A Aa Aa A a A AA Aa testcross: mating F1 generation to the parental (usually recessive) strain a a A Aa Aa ? aa aa a Aa aa Some genes have more than two alleles- Blood surface antigens Blood type also and ex. Of Codominance Sex-linkage basics Sex-linkage notes page Pedigree basics Pedigrees and pedigree analysis Sex-linked Pedigree