* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 1 Intro. To Genetics
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
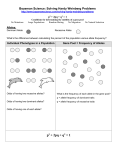
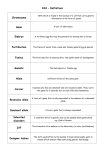
Biology 1 Intro. To Genetics We went over how to do a monohybrid punnett square. Hopefully you are okay with that – if not we can go over it when I get back For now, please copy the rest of these notes, so we can go over them a little faster when I get back Gene Interactions Gene – section of DNA that codes for a trait Allele – form of a gene either dominant (B) or recessive (b) There are a few exceptions to the Dominant / recessive alleles: 1. Incomplete dominance 2. Codominance 3. Polygenic inheritance 4. Sex linked traits 1. Incomplete Dominance • 1760’s German scientist : Josef Kolreuter crossed a pure recessive bred white carnation with a pure bred dominant red carnation and got a pink carnation appeared like “blended” parent traits. When crossed pink f2 generation, he got 1/4 red, 1/4, white, 1/2 pink With Incomplete dominance the dominant allele doesn’t mask the recessuve allele and heterozygous is a “blending” between the 2 homologous parents. Co-dominance • Both alleles are expressed ( or are active) • Ex. cattle : cross red hair co-dominant with white hair and get a roan • (white-brown mix ) both colors are expressed. Another example is out blood type: Blood Type • Receive one allele from mom and one from dad. • There are 3 possible alleles that contribute to a person’s blood type • A – which has a particular carbohydrate attached to the surface of the RBC • B – which has a particular carbohydrate attached to the surface of the RBC • i – which has neither carbohydrate attached to the RBC • • • • • AA or AO = A blood type AB = AB blood type BO or BB = B blood type io or OO = O blood type 2. Polygenic Inheritance • Many traits are result of interaction of many genes Ex. different combination of enzymes produce different color eyes. • When the product of a gene (a specific protein) is being actively produced by a cell we say the gene is being expressed . Within an organism, some genes are rarely expressed, some are constantly expressed, and some are expressed for a time and they turn off. Ex. Height, weight, eye color, skin color, hair color 3. Sex Linked Traits • Any trait that is on the X or Y chromosome is sex linked is considered to be sex linked Pedigrees A pedigree is a tool used to trace a trait through a family. To make a pedigree you need to know specific symbols and how they are linked together The next slide is an example of symbols scientists use to make pedigrees. Copy all the symbols (and their meaning) down into your notes so we will be ready to make these when I get back