* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Science NJ ASK Review
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
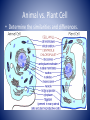
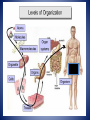
Life Science NJ ASK Review 8th Grade Science Animal vs. Plant Cell • Determine the similarities and differences. Animal • Lysosomes • Many small vacuoles • Nucleus is usually in the center • Rounded vs. Plant • Chloroplasts • Mitochondria • Ribosomes • Cell Walls • ER • Rough • One Large Central Vacuole • Smooth • Vacuoles • Nucleus usually pushed to • Nucleus • Nuclear Membrane the side • Cell Membrane • Usually rectangular(ish) • Cytoplasm • Golgi Apparatus What is a food chain? • A food chain is “a sequence of organisms, each of which uses the next, lower member of the sequence as a food source1” Important facts about food chains • In a food chain each organism obtains energy from the one at the level below. • Plants are called producers because they create their own food through photosynthesis • Animals are consumers because they cannot create their own food, they must eat plants or other animals to get the energy that they need. Four types of consumer • Herbivores: animals that eat only plants • Carnivores: animals that eat only other animals. • Omnivores: animals that eat animals and plants. • Detritivores: Animals that eat dead materials and organic wastes Other Ways to Classify Consumers 1. Primary Consumers: Herbivores. 2. Secondary Consumers: Carnivores that eat herbivores. 3. Tertiary Consumers: Carnivores that eat other carnivores. Identify the producer, one primary consumer, one secondary consumer and a tertiary consumer. Secondary Consumers Tertiary Consumers Primary Consumers Producer Hierarchy of Biological Classification Six Kingdoms Hierarchy of Biological Classification An easy way to remember… King = Kingdom Philip = Phylum Came = Class Over = Order For = Family Good = Genus Soup = Species • Which taxonomic group includes all the other groups? Kingdom • Human beings are most closely related to other animals that are in the same ________________. Species Organization of Living Organisms Cells -basic unit of an animal’s structure -become specialized _______________________________ Tissues -made of cells that work together to perform a specific function __________________________________________ Organs -made of different types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function ____________________________________________________ Organ Systems -made of organs that work together to perform a specific function _____________________________________________________________ Organisms Genetics - What are traits? • Physical Traits – Can be seen by others Eye color, hair color, height, left handed – Examples: • Acquired Traits – Learned skills – Examples: Playing a sport, riding a bike, playing a musical instrument • Behavioral Traits – Instinctual actions – Examples: Nest building and migration • Genotype Genetics The genotype is the specific genetic makeup of an individual, usually in the form of DNA. It codes for the phenotype of the individual. • Phenotype An individual’s observable traits. What people can SEE when they look at you • Allele Different forms of a gene, which produce variations of a genetically inherited trait. • An individual with non-identical alleles of a gene is heterozygous for that gene – Examples: Bb, Tt, Aa • An individual with identical alleles of a gene is homozygous gene – Examples: BB or bb, TT or tt for that Terms Used in Modern Genetics • A genetic factor that blocks another genetic factor is called dominant • A genetic factor that is blocked by the presence of a dominant factor is called recessive • An allele is dominant if its effect masks the effect of a recessive allele paired with it – Capital letters (A) signify dominant alleles; lowercase letters (a) signify recessive alleles – Homozygous dominant (AA) – Homozygous recessive (aa) – Heterozygous (Aa) Generation 1 B B b b In this case we have a dad with black fur and a mother with white fur. Because black is the dominant gene, we write it with a capital ‘B’. White fur is a recessive trait. It is written with a lowercase ‘b’. It does not matter what letter we choose to represent a gene, but capital letter is always dominant and lowercase is always recessive. Tongue Curling T=can curl T=cannot curl T t T T Copy into your notebook and complete the Punnett’s Square. What percentage of offspring will be able to curl their tongue?