* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LEQ: How do genes assort independently?
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
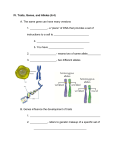
LEQ: How do genes assort independently? 9.4 to 9.6 Homologous Chromosomes Each chromosome of a homologous pair carries a copy for the same gene. For most genes there are two alleles. What would be the exception? Traits on sex chromosomes. The alleles can be the same Homozygous The alleles can be different Heterozygous Dihybrid Cross Genetic Cross of individuals differing in 2 traits 16 boxes Determine possible gametes A with P, A with p, a with P and a with P Keep alleles together (A with A and P with P) Capitol letter before lowercase Independent Assortment Independent Assortment When Mendel conducted dihybrid crosses he noticed new gene combinations (different from the P and F1) From that he came up with the Law of Independent Assortment: Each pair of alleles segregates independently from other pairs of alleles during gamete formation The genes did not have to be inherited together Independent Assortment When do genes independently assort? Metaphase 1 of Meiosis Test Cross A cross between an individual of unknown (homozygous dominant or heterozygous) genotype and a homozygous recessive individual If any offspring are recessive, then… Unknown is heterzygous If all offspring are dominant, then… Unknown is homozygous