* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CG7b-PSSM
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
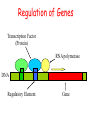
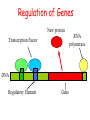
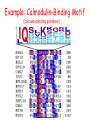
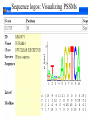
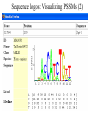
Intro to Probabilistic Models PSSMs Computational Genomics, Lecture 6b Partially based on slides by Metsada Pasmanik-Chor Biological Motives A large number of biological units with common functions tend to exhibit similarities at the sequence level. These include very short “motives”, such as gene splice sites, DNA regulatory binding sites, recognized by transcription factors (proteins that bind to the promoter and control gene expression), microRNAs, and all the way to protein families. Often it is desirable to model such motives, to enable searching for new ones. Probabilistic models are very useful. Today we deal with PSSM - the simplest. Promoter… Regulation of Genes Transcription Factor (Protein) RNA polymerase (Protein) DNA Regulatory Element www.cs.washington.edu/homes/tompa/papers/binding.ppt Gene Regulation of Genes Transcription Factor (Protein) RNA polymerase DNA Regulatory Element Gene Regulation of Genes New protein RNA polymerase Transcription Factor DNA Regulatory Element Gene Motif Logo • Motifs can mutate on less important bases. Position: 1234567 • The five motifs at top right have mutations in position 3 and 5. • Representations called motif logos illustrate the conserved regions of a motif. http://weblogo.berkeley.edu http://fold.stanford.edu/eblocks/acsearch.html TGGGGGA TGAGAGA TGGGGGA TGAGAGA TGAGGGA Example: Calmodulin-Binding Motif (calcium-binding proteins) PSSM Starting Point • A gap-less MSA of known instances of a given motif. Representing the motif by either: 1. Consensus. 2. Position Specific Scoring Matrix (PSSM). Consider now a specific “motives server”, called Consite. Sequence logos: Visualizing PSSMs Sequence logos: Visualizing PSSMs (2)