* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Mutations
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
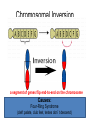
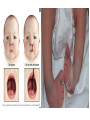
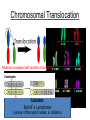
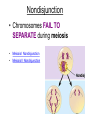
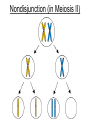
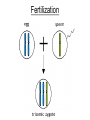
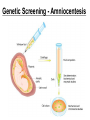
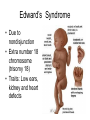
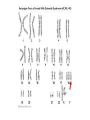
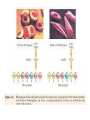
Human Genetic Mutations 2 Main Types of Mutations 1.) Chromosomal Mutations 2.) Gene Mutations What are chromosomes? • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome from each parent. • The chromosomes are coiled up DNA. • Under normal conditions all of the chromosomes are inherited in tact. Chromosomal Mutations • Any change in the structure or number of chromosomes • Large scale: Affect many genes 5 Types 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Deletion Duplication Inversion Translocation NonDisjunction Chromosomal Deletion One or more genes are removed Causes: Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (severe mental retardation) cri du chat syndrome (meowing sounds, mental retardation) Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS) refers to a condition that is caused by a missing part (deletion) of the short arm of chromosome 4. Chromosomal Duplication A segment of genes is copied twice and added to the chromosome Causes: Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (high arched foot, claw feet, confined to a wheelchair) Chromosomal Inversion a segment of genes flip end-to-end on the chromosome Causes: Four-Ring Syndrome (cleft palate, club feet, testes don’t descend) Chromosomal Translocation Material is swapped with another chromosome Causes: Burkitt’s Lymphoma (cancer of the lymph nodes, in children) Nondisjunction • Chromosomes FAIL TO SEPARATE during meiosis • Meiosis I Nondisjunction • Meiosis II Nondisjunction Nondisjunction • Produces gametes (and therefore a baby) with one missing chromosome or one extra chromosome Nondisjunction (in Meiosis II) Fertilization Nondisjunction • Every cell in that baby’s body will have __ copies of this chromosome instead of___. • This condition is called ____________. • Trisomy 21 = Individual has _____ copies of chromosome # ________ Nondisjunction • Every cell in that baby’s body will have 3 copies of this chromosome instead of 2. • This condition is called __________. • Trisomy 21 = Individual has _____ copies of chromosome # ________ Nondisjunction • Every cell in that baby’s body will have 3 copies of this chromosome instead of 2. • This condition is called TRISOMY • Trisomy 21 = Individual has __ copies of chromosome # ____. Nondisjunction • Every cell in that baby’s body will have 3 copies of this chromosome instead of 2. • This condition is called TRISOMY • Trisomy 21 = Individual has 3 copies of chromosome # 21. Chromosomal Mutations • Most chromosomal mutations are lethal • If the fetus survives: Tend to cause wide-spread abnormalities • Example: Down Syndrome Down Syndrome • Cause: Nondisjunction of chromosome 21 • Three copies of chromosome 21 = “TRISOMY 21” • One in every 691 babies in the the United States is born with Down syndrome, making Down syndrome the most common genetic condition. • Short stature (height) • Low muscle tone • A short, wide neck. • Slanted eyes. • Irregularly shaped mouth and tongue. • Intellectual disability • Heart defects Genetic Screening - Amniocentesis Karyotypes • A pictorial display of metaphase chromosomes from a mitotic cell • Homologous chromosomes- pairs • Chromosomes pairs 1-22 are called autosomes • Chromosome pair 23 are called the sex chromosomes Trisomy 21 - Down Syndrome Klinefelter’s Syndrome • Due to nondisjunction • Chromosome makeup is XXY • Creates a sterile male Turner’s Syndrome • Due to nondisjunction • Monosomy- the condition in which there is a missing chromosome. • Sex chromosome make up is X only • Females that will not undergo puberty. Edward’s Syndrome • Due to nondisjunction • Extra number 18 chromosome (trisomy 18) • Traits: Low ears, kidney and heart defects Patau’s Syndrome • Extra number 13 chromosome (trisomy 13) • Traits: Deformed eyes, ears and lips, polydactyly (extra fingers or toes) KEY POINT #1 Too much or too little DNA is bad! Gene Mutations • Small scale: one gene is affected • Any change to the DNA sequence of a gene: Nucleotides/Bases may be added, missing, or changed Gene Mutations: 2 Types Point Mutation Frameshift Mutation Point Mutation • One base (A, T, C, or G) is substituted for another • Can Cause: Sickle-cell anemia • 3 Possible Consequences: – nonsense mutations: code for a stop, which can translate the protein – missense mutations: code for a different amino acid – silent mutations: code for the same amino acid Frameshift Mutation • One or more bases (A, T, C, or G) are added or deleted • Can Cause: Cystic Fibrosis • Caused by: – Insertion: adding a base – Deletion: removing a base Causes of Mutations • spontaneous • occur during DNA replication • Caused by MUTAGENS • physical ex: radiation from UV rays, X-rays or extreme heat • chemical (molecules that misplace base pairs or disrupt the helical shape of DNA). Gene Mutations • KEY IDEA: A mutated gene will make a mutated protein Example: Sickle Cell Anemia Normal Red Blood Cell • Red blood cells shaped like a disc • Hemoglobin (protien) carries oxygen to all parts of the body Sickle Red Blood Cell • • • • • • Red blood cells form an abnormal crescent shape Hemoglobin (protein) is abnormally shaped don't move easily through your blood vessels form clumps and get stuck in the blood vessels Mutation located on Chromosome 11 Effects mostly African Americans Example: Cystic Fibrosis (CF) • What is it? – Autosomal, recessive disorder found on Chromosome 7 • Symptoms – Thick mucus in the lungs and digestive track – Constant lung infections and impaired digestion Cystic Fibrosis (CF) • Who gets it? – Most common in Caucasians • Prevalence – 1 in ~3,000 Americans has CF – 1 in 23 white Americans carries the mutant allele! Cause of Cystic Fibrosis (CF) • The “CFTR” gene is mutated – 3 base pairs are deleted • Mutant protein is missing an amino acid and cannot fold correctly vs Albinism • Due to the lack of the pigment melanin (a protein) in the skin, eyes, and hair. Hemophilia • Disorder that is linked to the sex chromosomes • Missing a protein needed for the blood to clot Tay-Sachs Disease • Inability to synthesize an enzyme that prevent lipid buildup in brain cells. • Causes the breakdown of nervous system Phenylketonuria (PKU) • Inability to code for an enzyme needed for changing the amino acid phenylalanine to tyrosine. • Damages brain cells and causes mental retardation. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy • Linked to the sex chromosomes • Results in the progressive weakening and loss of skeletal muscle. Colorblindness • Carried on the X of the sex chromosomes. • Occurs more frequently in males than females. KEY POINT #2 Mutation of a gene = Mutant protein Dysfunctional proteins cause the symptoms of the disorder