* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proetomics and Signaling
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
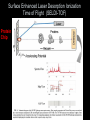
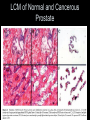
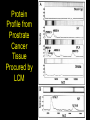
Sequencing of Mammalian Genomes Predicts 30,000 genes 2001 2002 What is the Proteome • All the proteins expressed in a particular cell or tissue. • By definition this will vary by tissue and cell type. – – – – – Cardiovascular Neuromuscular Islet cell Endothelial cell Muscle cell Why Study Proteomics? • Gives a better understanding of the function of gene products. • Allow for the design of rational drug therapies. • Provide new and specific markers of disease. Will Proteomics Provide a Stronger Means to Stratify Disease YES Greater Complexity=Greater Specificity Protein Modifications Phosphorylation Glycosolation Ubiquitination Cleavage Lipid etc. Dictates Function and Intracellular Localization 30,000 Genes How Many Proteins? 30,000 genes 4-6 splice variants 120,000 possible mRNAS >200 Post-translational Modifications 24,000,000 Possible Protein Isoforms 2,000,000 Predicted Proteins How Gene and Protein Expression is Regulated or Modified from Transcription to Post-translation Synaptojanin 2 Biomarker ID vrs Protein ID • • • • • BIOMARKER CHANGE +/IDENTITY ? SPECIFIC EASE BODY FLUID • • • • • PROTEIN INTERACTION PRESENCE ISOFORMS MODIFICATIONS FUNCTION Using Proteomics to Identify Biomarkers of Disease How do You ID Biomarkers • 2D-PAGE MALDI-TOF MS • ICAT MALDI-TOF MS • SELDI-TOF MS Proteomic flow 1D and 2D gels Proexpress Imager Propicker Progest Q Star XL -MS/MS-TOF Vision Station Biacore ProMS ICAT (Isotope Coded Affinity Tag) Deuterium Biotin Linker Thiol Reactive Group ICAT Provides Relative Levels of Expression Between Two Proteins Which is Reflected by the Ratio of the Amount of Peptide Surface Enhanced Laser Desorption Ionization Time of Flight (SELDI-TOF) Protein Chip Protein Chip Different Protein Profiles from Different Chip Surfaces Laser Capture Microscopy Allows for the Dissection of Cells Directly from Sectioned Tissues LCM of Normal and Cancerous Prostate Protein Profile from Prostrate Cancer Tissue Procured by LCM Do we Need all Three Approaches? • 2D-PAGE MALDI-TOF MS – Greatest resolving power – Large data base – Labor and time consuming • ICAT MALDI-TOF MS – Mostly abundant proteins – Needs cysteine residue • SELDI-TOF MS – Resolves from 8-50 kDa – Small amounts of sample