* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Proteins
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
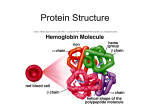
PROTEINS An Introduction to Structure and Functions of Proteins MALDI-TOF MS LAB • Question? – WHAT PROTEIN IS IT? • Strategy – Determine Molecular Weight (molar mass) using MALDI-TOF MS – Break it down (digest) with trypsin – Identify fragment by MALDI-TOF – Use data base to match fragments with data base fragments of protein digest 1 Proteins play key roles in living systems • Examples of protein functions Alcohol dehydrogenase oxidizes alcohols to aldehydes or ketones – Catalysis: Almost all chemical reactions in a living cell are catalyzed by protein enzymes. – Transport: Some proteins transports various substances, such as oxygen, ions, and so on. Haemoglobin carries oxygen – Information transfer: For example, hormones. – Control of genetic expression: Insulin controls the amount of sugar in the blood stream Transcription factors Amino Acid: Basic Unit of Protein R H3N+ C Amino group H Different side chains*, determine the COO- R, properties of 20 Carboxylic acid group amino acids. An amino acid Main Chain (backbone) Atoms(Cα,C=0,N) 2 Primary Structure Biosynthesis proceeds for the N-terminal to the C terminal of the protein. Stabilize tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins Create an organic solvent-like environment in the interior 3 Acid-base chemistry Salt bridges builders Lewis bases (ligands for metal ions) Hydrogen bonds Other dipole-dipole interactions Lewis bases (Coordination Chemistry) Redox chemistry (cysteine) 4 Hierarchical nature of Protein Structure Primary structure (Amino acid sequence) ↓ Secondary structure (α-helix, β-sheet) ↓ Tertiary structure (Three-dimensional structure formed by assembly of secondary structures) ↓ Quaternary structure (Structure formed by more than one polypeptide chains) Basic 3D structural units of proteins: Secondary structure α-helix β-sheet Secondary structures, α-helix and β-sheet, have regular hydrogen-bonding patterns. Antiparallel 5 Antiparallel Beta Sheet (arrows) Three-dimensional structure of proteins Tertiary structure Quaternary structure 6 Acid-Base Chemistry Effect of primary structure: important for short side chains Effect of tertiary structure 7