* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sexual Preproduction and Meiosis
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
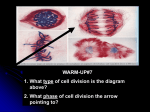
Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction • recombination of genetic material • More combinations means there is a higher chance at least some will survive a catastrophe • Offspring not identical to parents Sexual Reproduction • Union 2 haploid (1n) gametes (Such as Sperm and Egg)to form a diploid (2n) Zygote Diploid vs Haploid • These terms refer to the number of sets of chromosomes an organism has. • Humans are Diploid, we have two sets of chromosomes 46 total or 23 Pairs of “Homologous” chromosomes • Sperm and eggs are haploid they only have 23 chromosomes each. • When sperm and egg join the resulting zygote will have 46 chromosomes Homologous Chromosomes • Homologous means “Like” or “Same” • Homologous chromosomes are chromosomes that code for the same genes. Remember that a gene codes for a protein that may result in a trait. • The homologous chromosomes may have different version of the genes called “Alleles” They code for the same trait but may have different forms or colors. Meiosis • The process of making a haploid cell • Also known as a reduction division because the number of chromosomes is reduced in this process. • Two stages – Meiosis I – Meiosis II – Results in 4 haploid (1N) Gamates Meiosis I – DNA is Replicated – Homologous chromosomes line up in metaphase. – This is when genetic recombination can occur… so not all offspring from the same pair will be identical! Very important for variation within a population and for the rise of new species. – Results in 2 haploid cells Meiosis I Meiosis II – DNA in NOT replicated in the two haploid cells – chromatids separate and divide – results in 4 haploid (1n) cells. Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Meiosis II Anaphase II Meiosis I results in two The chromosomes line up in a The sister chromatids haploid (N) daughter cells, similar way to the metaphase separate and move toward each with half the number of stage of mitosis. opposite ends of the cell. chromosomes as the original. Telophase II Meiosis II results in four haploid (N) daughter cells.