* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download For example eye color (One gene from each parent).
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
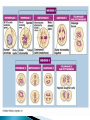
Chapter 11-4 Cell Division A thread-like structure containing genetic information. b. Tightly coiled DNA strands c. Homologous • Pairs of chromosomes that contain information for the same biological features. For example eye color (One gene from each parent). d. Tetrad • The structure made when the homologous chromosomes join. a. Cell division resulting in the number of chromosomes in a cell being divided in half, through the separation of homologous chromosomes. Diploid cells divide to produce haploid cells. a. b. • • c. Haploid – Cells that contain “half” the genetic information. One set of chromosomes. (n) Diploid – Cells that contain both sets of homologous chromosomes. (2n) Only occurs in reproductive cells. Cell division process similar to mitosis. d. • Occurs during the “M Phase” of the cell cycle. • Similar phases: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis • • • • • Unlike mitosis, MEIOSIS involves 2 divisions: Meiosis I and Meiosis II. a. • Produces 4 cells instead of 2. • Cells produced contain half the genetic information as the parent cell. b. Crossing Over: During prophase 1 the homologous chromosomes pair up and form tetrads, they also exchange genetic information. Gametes: Sex cells that contain half the genetic information (haploid) produced during meiosis. a. • • b. c. In males = sperm cells In females = egg cells (ova) Spermatogenesis: The process of making sperm cells. Occurs in the male reproductive organs, testes. Oogenesis: The process of making egg cells (ova). Occurs in the female reproductive organs, ovaries. d. Fertilization: The process of male and female haploid gametes (n) fusing to form a diploid zygote (2n).