* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 5
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
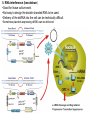
Chem 509 Signal Transduction Winter 2012 Lecture 5 1. Two-hybrid assay. •Created by Song and Fields. •Concept adapted from the studies of Ptashne •Modular nature of proteins. •Companies now make kits for this 2. IP Kinase activity assay •Assay employs immunoprecipitation technique. •Can use radiolabeled ATP or GTP •Can use Western blotting to detect phosphorylated substrate. 3. FRET (Förster resonance energy transfer) •Depends on transfer of energy from one molecule to another. (1-10 nm) •Requires two proteins to be modified and then expressed inside cells. •cyan fluorescent protein and yellow fluorescent protein are commonly used. • Comment on green fluorescent protein. •Detect by microscopy-makes pretty images. 4. Knockout mice •Powerful technique for determining the function of genes. •Assumes that human gene functions analogously in mice (not always true). P53 yes, RB no. •Knockin mice, transgenic mice •Conditional knock out mice 5. RNA interference (knockdown) •Good for tissue culture work. •Not easy to design the double stranded RNA to be used. •Delivery of the dsRNA into the cell can be technically difficult. •Sometimes plasmids expressing dsRNA can be delivered. 6. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) •Shows association and dissociation of large molecules (proteins) •Can calculate affinity constants and dissociation constants. •Requires expensive equipment. Nelson and Cox, Lehninger Biochemistry References Two hybrid assay: Fields S, Song O (1989). "A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions". Nature 340 (6230): 245-6. FRET: ^ Förster T. Zwischenmolekulare Energiewanderung und Fluoreszenz, Ann. Physik 6(2):55, 1948. Green fluorescent protein: Prendergast F, Mann K (1978). "Chemical and physical properties of aequorin and the green fluorescent protein isolated from Aequorea forskålea". Biochemistry 17 (17): 3448-53. Knockout mice: Capecchi MR. Generating mice with targeted mutations. Nat Med. 2001;7:1086-90. RNA interference: Fire, A., Albertson, D., Harrison, S., and Moerman, D. (1991) Production of antisense RNA leads to effective and specific inhibition of gene expression in C. elegans muscle. Development 113:503-514. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR): Aslan K, Lakowicz JR, Geddes C. Plasmon light scattering in biology and medicine: new sensing approaches, visions and perspectives. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 2005, 9:538–544. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP): Collas P, Dahl JA., Chop it, ChIP it, check it: the current status of chromatin immunoprecipitation. Front Biosci. 2008, 13:929-43.