* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetyltransferase wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
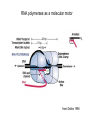
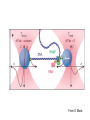
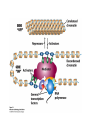
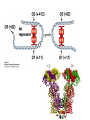
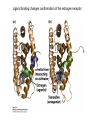
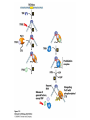
Lecture 12 RNA polymerase as a molecular motor Transcriptional control RNA polymerase as a molecular motor from Gelles 1998 From S. Block Average step size = 3.7A, which corresponds to the base spacing in BDNA RNAP can back-step! Transcriptional control (Chapter 7) DNA –> transcription –> RNA –> translation -> Protein The complexity and diversity of today’s forms of life are primarily due to two relatively simple types of physico-chemical phenomena: 1. Cooperative binding 2. Steric hindrance In bacteria: Even though lactose, arabinose and other sugars may be available for the cell, in the presence of glucose the production of enzymes metabolizing sugars other than glucose is repressed. This is known as catabolite repression. lac operon contains 3 genes necessary for consumption of galactose: (1) b-galactosidase, (2) galactoside permease and (3) thiogalactoside transacetylase There are positive and negative regulatory elements that make catabolite repression work. cAMP receptor protein (CAP), acting as a homodimer can bind both cAMP and DNA. When glucose is absent (high cAMP state), CAP binds to its positive regulatory element increasing transcription of the lac operon 50-fold. Lac repressor is a tetrameric complex that in the absence of lactose binds tightly to the operator region covering the transcription initiation site. In the presence of lactose or lactose mimicking substances (IPTG) it falls off. The Lac Operon High level of transcription takes place when glucose is low and lactose is high. Without bound activator (CAPcAMP) the lac promoter is poorly transcribed even when lactose concentrations are high and the Lac repressor is unbound (read section 7.1 for more information on prokaryotic gene control) Pax6 is a transcription factor responsible for development of several tissues. It utilizes 3 different promoters at distinct times during embryogenesis. Leucine Zipper and basic Helix-Loop-Helix proteins Ligand binding changes conformation of the estrogen receptor Cooperative binding of two unrelated transcription factors to a composite control element