* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Histone Modifications and Cancer
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
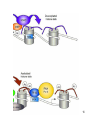
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
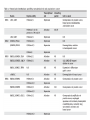
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
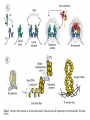
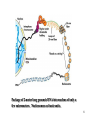
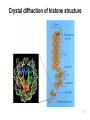
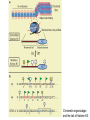
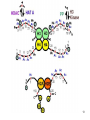
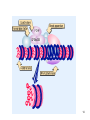
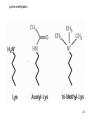
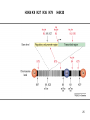
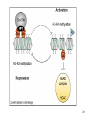
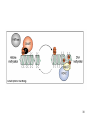
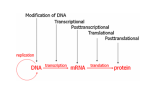
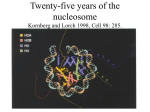
Histone Modifications and Cancer - Yu Zhang, Ph.D., (张瑜) - Institute of Genetics and Cytology, School of Life Sciences, - Northeast Normal University 1 • Histone code hypothesis • Histone acetylation and deacetylation • Histone lysine methylation • Argine methylation and transcriptional regulation • Histone modification in cancer • Epigenetic diagnosis and therapies of cancer 2 Definition of Epigenetics Heritable and/or acquired changes in gene expression that occur without changes in DNA sequence. 3 Histone code hypothesis 4 5 Package of 2-meter long genomic DNA into nucleus of only a few micrometers. Nucleosomes as basic units. 6 Crystal diffraction of histone structure 7 Chromatin organization 8 and the tail of histone H3. 9 The N-termini of core histones are active domains critical to DNA-protein interaction. Many specific amino acid residues in N-termini are subject to various covalent chemical modifications, such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, etc. 10 Various modifications at defined sites of the core histone N-termini constitute the “histone code”. 11 Histone acetylation and deacetylation 12 13 14 15 CHEST 129 1 JAUNARY 2006 16 TypeA HATs type B HATs localized in nuclei acetylate nucleosomal histones cytoplasmic fractions acetylating newly synthesized histones before chromatin assembly during DNA replication. Gcn5p and homologs PCAF, p300/CBP, TAFII250 and homologs, and SRC-1 and ACTR yeast Hat1p p300/CBP 17 Reversed acetylation modification 18 19 20 HDAC Class I Schematic Structure Rpd3p Amino Acids Year HDAC1 482 1996 HDAC2 488 1996 HDAC3 428 1998 HDAC8 377 2000 HDAC4 1084 1999 HDAC5 1122 1999 HDAC7 912 2000 HDAC6 1215 1999 HDAC9 673 2001 Class II Hda1p Class III Sir2-like deacetylases (NAD-dependent activity) 21 Histone acetylation/deacetylation • Acetylation/deacetylation of defined lysine residues of H3, H4, H2A and H2B histones; • Catalyzed by histone acetyltransferase/deacetylase complexes (HAT/HDAC); • Hyperacetylation (high) → open nucleosome and chromatin structure → transcription activation; • Hypoacetylation (low) → tight nucleosome and chromatin structure → transcription repression. • A balanced acetylation level of the genome is critical to the normal function of the cell and organism. 22 Histone lysine methylation 23 Lysine methylation 24 H3K4 K9 K27 K36 K79 H4K20 25 26 27 EZH2 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Thanks for your attention! 37