* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
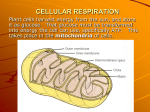
Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Both autotrophs and heterotrophs use the compounds in food for energy sources. Autotrophs make their own glucose. Heterotrophs cannot. The process by which glucose molecules are broken down to release energy (ATP) is cellular respiration. Cellular Respiration The process by which glucose molecules are broken down to release energy is cellular respiration. It is a series of chemical reactions that produces ATP. Most cellular processes use ATP for energy. Two types of Respiration There are two types of cellular respiration. Aerobic - requires oxygen Produces 36 ATP from each glucose Anaerobic - takes place without oxygen Produces 2 ATP from each glucose Anaerobes Anaerobes are organisms that use the anaerobic respiration pathway. Most anaerobes are bacteria. Anaerobes do NOT require oxygen. Aerobes Aerobes are organisms that use the aerobic respiration pathway. Aerobes require oxygen. Stages of Respiration The first stage of respiration for all living organisms, anaerobes or aerobes, is called glycolysis and it takes place in the cytosol. Glycolysis Glyco means “glucose/sugar” Lysis means “to split” glycolysis means “to split glucose” Glycolysis Glucose C6H12O6 Two pyruvate (3-C) molecules Two ATP Two NADH Stages of Respiration The second stage in aerobic respiration is the Krebs cycle, which occurs in the mitochondria. Pyruvate is converted to Acetyl-CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle. The Acetyl-CoA is broken down to form CO2, ATP, NADH, and FADH2. Stages of Respiration In the Krebs cycle, the pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA, which is broken down to form CO2, ATP, NADH, and FADH2. One ATP is produced for each pyruvate. CO2 is a byproduct. why we breathe out carbon dioxide! Stages of Respiration So, after glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, there are 4 ATP produced from each glucose. There’s still 32 ATP left to get from the process (because aerobic produces a total of 36 ATP from each glucose). Electron Transport Chain The rest of the energy is contained in electrons carried by NADH and FADH2. Electron transport is the process by which energy is transferred from NADH and FADH2 to ATP. This phase is also in the mitochondria. Aerobic Respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 glucose oxygen 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy carbon water ATP dioxide Aerobic Respiration Compare the reactants and products of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. The reactants of one process are the products of the other! Anaerobic Respiration Anaerobic respiration does NOT require oxygen. The 2 most common forms are: Alcoholic fermentation Lactic acid fermentation Alcoholic Fermentation Is carried out by yeast, a kind of fungus Does not require oxygen Uses only glycolysis Pyruvate + NADH Ethanol + NAD+ + CO2 Alcoholic Fermentation Uses: Baking Wine and beer industry Ethanol Swiss cheese Quic kTime™ and a TIFF (Unc ompres sed) decompress or are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this pict ure. QuickTi me™ and a TIFF ( Uncompressed) decompr essor are needed to see thi s p icture. QuickTi me™ and a TIFF ( Uncompressed) decompr essor are needed to see thi s picture. Lactic Acid Fermentation Uses only glycolysis Does not require oxygen Pyruvate + NADH Lactic Acid + CO2 Lactic Acid Fermentation Carried out by human muscle cells when they are oxygendeprived. Lactic acid is a toxin and causes fatigue, soreness, and stiffness in muscles. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.