* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNA: Early Life Forms?
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
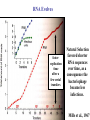
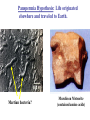
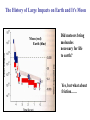
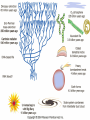
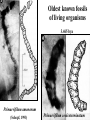
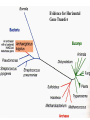
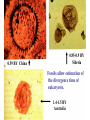
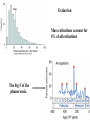
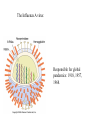
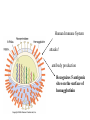
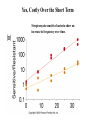
The Origin of Life Take home message: Science has not provided a step by step recipe for making life. Science has provided data to support some of the possible or necessary steps. What defines life? 1. Has a genotype (genetic blueprint that stores and transmits information). 2. Has form and function (i.e. phenotype: expression of genotype). 3. Life evolves. Oparin-Haldane Model for the Origin of Life Simple molecules Complex polymers H20, NH3, CO2 nucleotides, amino acids Nucleic acid RNA, DNA, protein Cellular life RNA: Early Life Forms? Intron in Tetrahymena phenotype genotype “Pick up the tail” Altman and Cech Evidence for RNA as an Early Life Form 1. Stores information and is catalytic 2. Basic component of: a. ribosomes and tRNA b. energy carrier molecules (ATP, GTP) c. electron-transfer cofactors (NAD, SAM) RNA Evolves faster replication time after a few serial transfers Natural Selection favored shorter RNA sequences over time, as a consequence the bacteriophage became less infectious. Mills et al., 1967 Test Tube Experiments Show: (1) RNA can evolve (via artificial selection) (2) Ribozymes have been selected to perform a number of protein-like tasks: phosphorylation, aminoacyl transfer, peptide bond formation, carbon-carbon bond formation However, can RNA self-replicate? (i.e. can an RNA dependent replicase be found?) But Where Did RNA Come From? Seems unlikely that RNA can be made in one step from inorganic molecules. Did a self-replicating system predate RNA? So, before RNA…. Where did simple organic molecules originate? Did Earth Have All of the Ingredients? Oparin-Haldane Model Simple molecules H20, NH3, CO2 Complex polymers (1) Was the prebiotic environment permissive? nucleotides, amino acids (2) How is this achieved in H20 given hydrolysis? Nucleic acid RNA, DNA, protein (3) How were membranes assembled? Cellular life (1) Was the pre-biotic environment permissive? Miller (1953): Assuming Atmosphere Reducing H2, CH4, and NH3 amino acids, sugars, nucleotides Mojzsis et al. (1999): Assuming Atmosphere Oxidizing C02, N2: aldehydes (ribose sugar in RNA) Oro’ (1961): Nucleotides from inorganic molecules HCN, NH3 adenine (2) How is this achieved in H20 given hydrolysis? Polynucleotides 40 nucleotides long have been synthesized using clay as a catalyst. montmorillonite, illite, and hydroxylapatite Panspermia Hypothesis: Life originated elsewhere and traveled to Earth. Martian bacteria? Murchison Meteorite (contained amino acids) The History of Large Impacts on Earth and It’s Moon Moon (red) Earth (blue) Did meteors bring molecules necessary for life to earth? Yes, but what about friction…… When was earth hospitable enough for life to evolve? Banded iron formation Greenland 3.85 bya magnatite silicate bands Apatite crystals (20 mm) (calcium phosphate minerals carbonaceous material carbonaceous speck with high C12 to C13 ratio What was the oldest common ancestor like? (cenancestor) a. Used DNA and amino acids to make proteins b. Cellular c. Structurally similar to filamentous cyanobacteria. Oldest known fossils of living organisms 3.465 bya Primaevifilum amonenum (Schopf, 1993) Primaevifilum conicoterminatum Phylogeny of all living organisms (small-subunit rRNA) Woese (1996) Evidence for Horizontal Gene Transfer Will it be possible to reconstruct the branching sequence at the root of the tree of life? 0.85-0.9 BY Siberia 0.59 BY China Fossils allow estimation of the divergence time of eukaryotes. 1.4-1.5 BY Australia 2 BY Eukaryotic Algae? Michigan Grypania spiralis Cambrian Explosion Evolutionary Diversification 543-506 mya Cambrian Explosion: All major body plans first made an appearance in the fossil record during a 40 my period Ediacaran Fuanas entirely soft-bodied organisms from 565 mya Brachina delicata Spriggina floundersi (sponges, jellyfish, comb jellies) New Fossil Finds are Pushing Back Estimates of Divergence Times Fossil embryos suggest precambrian diversification of bilateralians (Xiao et al. 1998) Possible flatworm or arthropod zygotes and embryos Burgess Shale Faunas 520 mya (trilobites, segmented worms, molluscs, chordates) New Fossil Finds are Pushing Back Estimates Of Animal Divergence Times (Shu et al. 1999) 530 my Cambrian vertebrate: Haikouichthys eraicunensis Small subunit RNA most basal earliest fossils Cambrian: Diversification of Animal Body Plans Symmetry a. Radial or asymmetrical: Diploblast (endoderm and ectoderm) b. Bilateral: Triploblast (endo, ecto, and mesoderm) Coelomate i. Protostomes ii.Deuterostomes Also: segmented body plans, shells, exoskeletons, appendages, notochords Was the Cambrian Explosion Explosive? Molecular clock estimates suggest 900-1200 my divergence times for the major animal groups (Wray et al., 1996). i.e. Major animal lineages were established pre - Cambrian. if so There should be fossil evidence! What Caused the Cambrian Explosion? Environmental change: Higher oxygen may have allowed for larger, energetically costly morphologies. Diversification of phytoplankton may have spurred the evolution of herbivores and predators. Genetic changes? Cloudina Stasis Is Evolution Too! Darwin’s View Punctuated Equilibrium (Gould and Eldridge, 1972) Jackson and Cheetham, 1994 Why Does Stasis Occur? not for lack of genetic variation dynamic stasis in pliocene bivalves Extinction Mass extinctions account for 4% of all extinctions The big 5 of the phanerozoic. Iridium concentration in clay layer at KT Boundary Other evidence: • Chicxulub crater • Microtektites • Soot deposits • Evidence of tsunami Habitat Destruction Current extinctions are occurring at 100 - 1000 times the normal or background rate. May et al. 1995, Pimm et al., 1995 Human Population by 2050 = 13 billion Evolutionary Applications in Medicine Ch 14 - pp 529-541 Cholera Epidemic of 1854 London, England Tuberculosis death rate as a function time The Influenza A virus: Responsible for global pandemics: 1918, 1957, 1968. Human Immune System attacks! antibody production Recognizes 5 antigenic sites on the surface of hemagglutinin Antigenic site: Specific parts of a foreign protein that the immune system recognizes and remembers. Do flu strains with novel antigenic sites enjoy a selective advantage? Divergence of Frozen Flu Samples Nucleotide divergence occurs at a remarkably constant rate for hemagglutinin. Phylogeny of Frozen Flu Samples A remarkably linear phylogenetic history. Distribution of Amino Acid Substitutions Antigenic Sites Surviving Lineages Extinct Lineages 33 31 NonAntigenic Sites 10 35 18 Codons in particular appear to be under strong Natural Selection How is this information used to develop Flu vaccines? Origin of Pandemic Flu Strains Nucleoprotein Gene Phylogeny of flu virus hemagglutinin genes What species did the 1968 flu likely derive? Phylogeny of flu virus hemagglutinin genes (cont) Hypothesis: Bird and human viruses recombine in pigs then infect humans. Bacteria and Antibiotics Evidence that Antibiotics Select for Resistant Bacteria -Possible to isolate resistant bacteria from patients that originate during antibiotic treatment -CDC survey (1994) data of tuberculosis patients: New Cases -Number with resistant bacteria 243 -Number with susceptible bacteria 2728 -Fraction resistant 8.2% Relapsed Cases 41 150 21.5% Frequency of penicillin resistance among Pneumococcus bacteria in Islandic children as a function of time Public reduced antibiotic use Evidence that Antibiotics Select for Resistant Bacteria Is Resistance Costly to Bacteria? (E. coli) Schrag et al (1997) Yes, Costly Over the Short Term Streptomycin-sensitive bacteria show an increase in frequency over time. What about the Long Term? Not Costly Over the Long Term Streptomycin-sensitive bacteria show a decrease in frequency over time. Judicious Use of Antibiotics -Avoid contracting foodborne bacteria -Limit use of antibacterial soaps and cleaners -Don’t request antibiotics for colds or flu -Take all of your antibiotic medicine -Wash hands to avoid spread of disease -Doctors should not prescribe antibiotics unless necessary -Doctors should prescribe antibiotics with specific target range -Doctors should isolate patients infected with resistant bacteria From Levy (1998)