* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download π- Stacking Interaction
Index of biochemistry articles wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Surround optical-fiber immunoassay wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembling peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
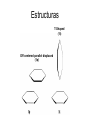
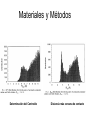
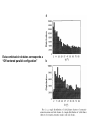
π- Stacking Interaction Ana Gabriela Murguía Carlos Villa π- Stacking Interaction • Proteínas no homologas • Difracción de Rayos X • Posición preferida y orientación de interacciones no covalentes • Aminoácidos Aromáticos (Cad. Laterales) • Dimeros π- Stacking Interaction • Agentes medicinales contienen sustituyentes aromáticos • El reconocimiento diferencial esta basado en las interacciones aromáticas Estructuras T-Shaped (1t) Off centered parallel displaced (1p) Hipótesis • En el core de la proteína (Hidrofobico) en el estado sólido, las propiedades dinámicas de la interacción bencenobenceno están satisfechas y una estructura preferida prevalece, aunque…………………………… Dímero de Benceno Materiales y Métodos Determinación del Centroide Distancia más cercana de contacto Esta combinación de datos corresponde a “Off centered parallel configuration” La forma de la distribución Y puede ser extrapolada a una distribución de Boltzman, bajo ciertas asunciones Resultados • La estructura paralela descolocada es mas estable que la estructura con forma T • La diferencia de la energia es dependiente del seno y • La tempertura es 300K Discusión • La estructura paralela descolocada es mas estable que una estructura de forma T en 0.5 – 0.75 kcal/mol • Phe-Phe en 1.0 kcal/mol • Otros autores dicen lo contrario (además que no existen en proteínas) Quizás debido a descuido en la distribución de los ángulos Aromatic Interaction • π-π interaction is a noncovalent interaction between organic compounds containing aromatic moieties. • π-π interactions are caused by intermolecular overlapping of p-orbitals in π-conjugated systems, so they become stronger as the number of πelectrons increases. The role of -stacking in self-assembly processes • Many areas of chemistry and biochemistry, most notably in molecular recognition and self-assembly. • Aromatic rings tend to form high-order clusters of four different types: parallel displaced, Tshaped,parallel staggered, or Herringbone. Amyloid formation • • • • • • Alzheimer’s disease (AD) Diabetes mellitus (type II) Prion diseases Familial amyloidosis Light chain amyloidosis Formation is a process in which normal wellfolded cellular proteins undergo a self-assembly process that leads to the formation of large and ordered protein structures. Aromatic residues in short amyloid related peptide Islet amyloid polypeptide • Minimal amyloid-forming fragment of the 37 amino acid islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), or amylin. • IAPP deposits found postmortem in 95% diabetes. • Peptide form amyloid fibers in vitro. • 6 residue peptide fragment of human IAPP (NFGAIL) form amyloid fibrils similar to the fulllength protein. • 5 residue fragment (FGAIL) forms ordered amyloid fibrils, are different in morphology from the full-length peptide. • A shorter peptide corresponding to the GAIL sequence did not form any fibrils at all. Alzheimer’s -amyloid • Brain senile amyloid plaques composed of the AB peptide • Short fragment of AB contains 2 phenylalanine residues (QKLVFF) was shown to bind specifically to full-length peptide. • The short peptide could inhibit amyloid formation by the full-length AB polypeptide. • LVFFA and its derivatives and LPFFD • KLVFFAE, forms amyloid fibrils. • Amyloid fibrils process of Molecular recognition and self-assembly, the high affinity and selectivity of the FF motif seems to provide the molecular recognition. Aortic medial amyloid • Aromatic residues is the octapeptide fragment (NFGSVQFV) of the 364 amino acid lactadherin protein. • Amino acid sequence analysis of the 5.5 kDa peptide demonstrated that derived from an integral proteolytic fragment of lactadherin. • Was synthesized and characterized form amyloid deposits Animal and yeast prions • Animal prion diseases are sporadic or inherited neurodegenerative disorders that are transmitted by a protein infective agent. • The agent is a misfolded form (PrS) of a normal cell protein (PrP) that acts by a conversion of normal folded PrP proteins to amyloid-like aggregates. • The importance of the octapeptide repeats is the fact result from the insertion of one to nine extra octapeptide repeats in addition to the five repeats that occur in the normal prion protein. • A misfolded variant in yeast (Sup35p) of a normal cellular protein (Sup35), which has been shown to cause a change in the phenotype of a normal cell by converting the normal protein into aggregates. The role of -stacking interactions in chemistry • Amyloid fibril formation is basically a process of intermolecular recognition and self-assembly, the -stacking can provide: • 1) an energetic contribution that stems from the stacking itself; such a contribution can thermodynamically drive the self-assembly process, • 2) specific directionality and orientation provided by the specific pattern of stacking. Cont … • The mechanism of amyloid includes a stepwise assembly of short recognition elements. • At the first stage, 2 structural elements that contain aromatic residues form a bimolecular structure, which is restricted by the allowed geometry of - stacking. • Followed by a stepwise addition of further monomers containing the same recognition elements. • Again, the overall structural organization of the addition process is being directed by the restricted geometries of the stacking interaction.