* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download From DNA to Protein
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
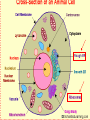
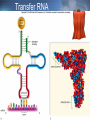
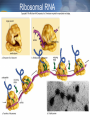
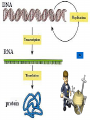
From DNA to Protein Chapter 14 Part III Translation • review of RNA • translation: process of converting information in mRNA into sequence of amino acids to make a protein • occurs at the ribosomes in the cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum The Cell Players in Translation • tRNA – each tRNA carries one amino acid on one end of the compound •An anticodon on the other end identifies the codon in mRNA that codes for the amino acid •rRNA makes up the ribosomes and provides the bonding sites •E (for exit) site •P (for peptide) site •A (for amino acid or acceptor) site Transfer RNA Ribosomal RNA Step #1 of Translation: Initiation • Parts needed: • ribosome (large and small) • initiation factors (proteins), and • mRNA and initiator tRNA •UAC anticodon; carries met • small rRNA attaches to mRNA (at start codon – AUG) • Initiator tRNA attaches to P site • large rRNA joins small rRNA Initiation Step #2 of Translation: Elongation • growth in length of the polypeptide • tRNA bring amino acids to ribosome • ribosome reads codon in mRNA •allows 1 tRNA with anticodon complementary to mRNA codon to bring amino acid •joins the ribosome at A site • methionine of initiator is connected to amino acid of 2nd tRNA by peptide bond Elongation continued • next tRNA moves to P site (translocation) • initiator moves to E site and exits • ribosome reads the next codon • allows 1 tRNA to bring its amino acid (anticodon matches mRNA codon) and joins the ribosome at it’s A site • dipeptide on 2nd amino acid is connected to amino acid of 3nd tRNA by peptide bond Elongation Step #3 of Translation: Termination • previous tRNA moves to P site • spent tRNA moves to E site (exits) • ribosome reads STOP codon • UAA, UAG, UGA – no amino acid • polypeptide (protein) released by release factor • ribosome releases mRNA and dissociates into subunits • mRNA can read by another ribosome Termination Final Thoughts • DNA makes RNA makes proteins • mRNA strands can be read several times to make proteins • Proteins must fold in a specific way to fit their function • Proteins go anywhere in the cell to provide structure or act as enzymes THE END