* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
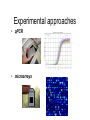
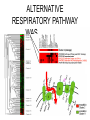
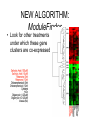
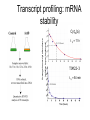
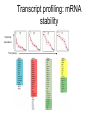
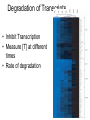
Experimental approaches • qPCR • microarrays VISUALISATION OF EXPRESSION DATA CLUSTER ANALYSIS RESULTS: CLUSTER ANALYSIS • Co-expressed gene clusters • Associations not previously reported • Functionally related genes co-induced: – evidence for induction of specific biological pathways ALTERNATIVE RESPIRATORY PATHWAY WAS INDUCED SUBSTRATE TRANSPORT WAS REPRESSED v| Entry of substrates into mt Limit availability of substrates for ETC? …limit flux through ETC …limit ROS production/oxidative damage AMINO ACID METABOLIC PATHWAYS WERE INDUCED Amino acid metabolism BRANCHED CHAIN AMINO ACID PATHWAYS INDUCED Branched chain amino acids BCAT Branched chain a-keto acids BCKDC * Branched chain amino acid metabolism Acyl-CoA IVD MCCAse 3-methyl-gluteconyl-CoA E-CoAH Acetoacetate + Acetyl-CoA * Enoyl-CoA * * E-CoAH Hydroxy-acyl-CoA Val Leu Ile HIBDH * Propionyl-CoA Propionyl-CoA + Acetyl-CoA Image adapted from: Taylor et. al. (2004) Plant Physiol 134(2): 838-48. PROBLEMS WITH CLUSTERING • Good at identifying genes that are coexpressed in response to all/most treatments • Not good at identifying genes that are co-expressed in response to specific subsets of treatments PROBLEMS WITH CLUSTERING Treatments Genes Genes Treatments NEW ALGORITHM: ModuleFinder • Choose an initial subset of treatments • Identify subset of genes that are coexpressed in response to these treatments • Cluster into groups NEW ALGORITHM: ModuleFinder • Look for other treatments under which these gene clusters are co-expressed RESULTS: ModuleFinder NDB2 Amino acid synthesis AOX1a carriers All associated with: flux through ETC ATP synthase activity ROS Classical ETC components Research focus - mitochondria protein import replication, transcription & translation biosynthetic pathways amino acids nucleotides vitamins folate lipids heme TCA cycle respiratory chain membrane transport Transcript profiling: import components TIM17 TIM22 TIM23 TOM7 TIM44 TOM9 TIM16 TOM20 TOM40 MPP TIM14 Transcript profiling: mRNA stability (relative to pre-treatment) Average transcript abundance Cytc(a) t ½ = 11 h TIM22-3 t ½ = 54 min Transcript profiling: mRNA stability Transcript abundance Time (hours) Degradation of Transcripts • Inhibit Transcription • Measure [T] at different times • Rate of degradation