* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metabolic Energy - Metabolism Foundation
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
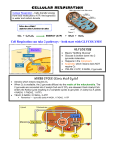
Metabolic Energy for Dummies: A quick look at Cellular Metabolism (Energetics) By Richard Belicek Introduction: This presentation will cover the general steps that nutrient sources take to be utilized by the body and how energy is created through metabolism. What is Metabolism? metabolism defined: the total chemical activity and flow of resources that occurs within an organism’s boundary. Where does it start? Nutrient sources from food. Foods such as steak, pizza, salad, ice cream and chocolate are broken down into these MACROMOLECULES: Proteins Fats Carbohydrates Macromolecules to Simple Subunits Proteins = Amino Acids Fats = Fatty Acids and Glycerol Carbohydrates = Simple Sugars Subunits follow metabolic pathways Amino Acids >Protein catabolism = Acetyl CoA >Gluconeogenesis = Pyruvate Fatty Acids and Glycerol >Oxidation = Acetyl CoA >Gluconeogenesis = Pyruvate Simple Sugars (Glucose) >Glycolysis =Pyruvate Glycolysis The sequence of rxns that convert glucose into pyruvate Glycolysis Occurs in the Cytoplasm Aerobic or Anaerobic Glucose enters the glycolytic pathway ATP: gross= 4, net= 2 NAD = 2 NADH, transported to the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) The Krebs Cycle aka: Tricarboxcyclic Acid Cycle or Citric Acid Cycle. Krebs Cycle Pyruvate enters cycle 2 cycles per Pyruvate molecule 1 ATP is produced per cycle NAD and FAD = 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 NADH and FADH2 are transported to the (ETC) Electron Transport Chain Electron Transport Chain Occurs in the Cristea of the mitochondria NADH and FADH2 are oxidized Hydrogen and electrons are carried along chain transfer energy Electrochemical gradient = ATP O2 final acceptor = H2O Electron Transport Chain (1 NADH = 3 ATP, 1 FADH2 = 2 ATP) Krebs Cycle = 8 NADH = 24 ATP = 2 FADH2 = 4 ATP For glycolysis (1 NADH= 2 ATP) Glycolysis = 2NADH = 4 ATP Overview: Summary Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Total ATP = 36 net NO Questions, Thank you. HOORAY! Thank you Have a good break!!