* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 19_12_13rw
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
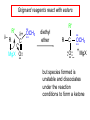
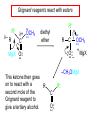
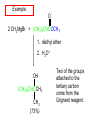
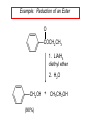
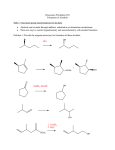
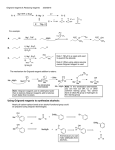
19.12 Reactions of Esters with Grignard Reagents: Synthesis of Tertiary Alcohols Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Grignard reagents react with esters – R R' •• + OCH 3 •• C MgX O •• •• R' diethyl ether R C •• OCH3 •• • O • + MgX • •• •– but species formed is unstable and dissociates under the reaction conditions to form a ketone Grignard reagents react with esters – R R' •• + OCH 3 •• C R' diethyl ether R OCH3 •• • O • + MgX • •• •– MgX O •• •• This ketone then goes on to react with a R second mole of the Grignard reagent to give a tertiary alcohol. C •• –CH3OMgX R' C O •• •• Example O 2 CH3MgBr + (CH3)2CHCOCH3 1. diethyl ether 2. H3O+ OH (CH3)2CHCCH3 CH3 (73%) Two of the groups attached to the tertiary carbon come from the Grignard reagent. 19.13 Reaction of Esters with Lithium Aluminum Hydride Reduction of Esters Gives Primary Alcohols Lithium aluminum hydride preferred for laboratory reductions. Sodium borohydride reduction is too slow to be useful. Catalytic hydrogenolysis used in industry but conditions difficult or dangerous to duplicate in the laboratory (special catalyst, high temperature, high pressure). Example: Reduction of an Ester O COCH2CH3 1. LiAlH4 diethyl ether 2. H2O CH2OH + (90%) CH3CH2OH