* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chap20 Grignard reagents
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
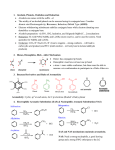
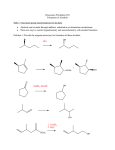
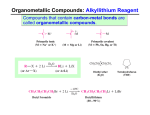
Grignard reagents & Reducing reagents R X Mg°/THF or Et 2O 2/22/2016 E+ R Mg X +Mg O δ+ H OR' E+ = R– R E R δ+ R' R δ+ OR2 O H 3C Mg°, THF Br A. R Open Here X For example: O O R2 ≠ H CH 3 MgBr H 3C H 3C H+ O— OH CH 3 CH 3 I B. 1) Mg°, Et 2O D 2) D 2O I C. HO 1) Mg°, Et 2O Ph O 2) MeO Note 1: NH 4Cl is a weak acid used to quench the alkoxide Note 2: When using esters assume excess Grignard reagent is used Ph 3) NH 4Cl The mechanism for Grignard reagent addition to esters: O O Me MgBr MeO H – OMe MeO Et Me the tetrahedral intermediate Et O Me O H O Et Me OH Et Me Me Et Me Me MgBr Note: In the tetrahedral intermediate, you can kick out OR, Cl, or other common leaving group. You cannot Note: Grignard reagents add to aldehydes faster have an alkyl (R) group or hydrogen as than to ketones Grignard reagents add to ketones the leaving group much faster then to esters Using Grignard reagents to synthesize alcohols: Nearly all carbon-carbon bonds at an alcohol functional group could be prepared using Grignard technologies. OH Me OH Me BrMg O Me Br + H BrMg or O MeMgBr + H OH H H + And because you can make aldehydes from alcohols... O H H Grignard reagents & Reducing reagents 2/22/2016 Retrosynthetic analysis tips: OH R R comes R O + RMgBr OR R from Cl RMgBr + MeO O OMe R =R =R OH R R R1MgBr R1 O + R R OH R O R1 O RMgBr + OR R1 Cl Note: OMe represents any ester R =R R RMgBr + MeO OR R1MgBr R1 2 O + R O R2 Then R H OH R2 R2 H R2 R O + RMgBr For Example: O OH Me MeO H O H O + O MeO H O Me O ClMg H O Three last notes on Grignard reagents: 1) Grignard reagents are nucleophiles that add to the specific types of electrophiles shown in this handout (ie. that are not generally used for SN 2 reactions on alkyl halides). 2) Alkyl Na, Li, and K reagents (i.e. H 3CC CNa ) react very similarly to Grignard reagents. 3) An R – addition to a carbonyl is a reduction just like a hydride H – delivered from BH 4— H2 Reducing Reagents Na, Li, or K : Used to reduce alkynes to trans-alkenes BH 3 : Adds to alkenes and alkynes (reducing them) With the CBS Catalyst, reduces ketones to alcohols, enantioselectively Selectively reduces carboxylic acids to alcohols (Does react with esters) NaBH 4 : Reduces aldehydes, acid chlorides, and ketones to the corresponding alcohol (reduces esters very slowly) LiBH 4 : Reduces esters, ketones, acid chlorides, and aldehydes to the corresponding alcohol LiAlH([OC(CH 3)3]3 : Used to reduce acid chlorides and esters (at –78 °C) to aldehydes (stops at the aldehyde!) Reduces ketones, acid chlorides,and aldehydes to the corresponding alcohol i-Bu2AlH (DIBAL): Used to reduce esters and acid chlorides (at –78 °C) to aldehydes (stops at the aldehyde!) Reduces ketones, acid chlorides,and aldehydes to the corresponding alcohol LiAlH 4 : (LAH) Very powerful reducing agent also reduces carboxylic acids Reduces ketones, acid chlorides,and aldehydes to the corresponding alcohol Reduces amides to the corresponding amine