* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Synthesis of Alcohols Using Grignard Reagents Grignard reagents
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
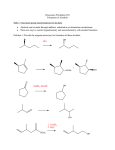
Synthesis of Alcohols Using Grignard Reagents Grignard reagents act as nucleophiles toward the carbonyl group δ– R δ+ C diethyl ether R C + •O• MgX • • •• – MgX O •• •• H3O+ two-step sequence gives an alcohol as the isolated product Grignard reagents react with: formaldehyde to give primary alcohols aldehydes to give secondary alcohols ketones to give tertiary alcohols esters to give tertiary alcohols R Grignard reagents react with: formaldehyde to give primary alcohols C • OH • •• Grignard reagents react with formaldehyde H δ– R δ+ H C diethyl ether H R C H •• O •• •• – MgX O •• •• + MgX H3O+ product is a primary alcohol Example diethyl ether CH3(CH2)3C MgCl C • OH • •• CH + CH3CH2MgBr MgBr diethyl ether H C O H CH2OH R Using Acetylenic Grignard Reagents Mg Cl H H3O+ CH2OMgCl (64-69%) Grignard reagents react with: formaldehyde to give primary alcohols aldehydes to give secondary alcohols CH3(CH2)3C CMgBr MgBr + CH3CH3 1. H2C O 2. H3O+ Can you use a different reaction CH3(CH2)3C CCH2OH other than a Grignard? Grignard? (82%) H Example Grignard reagents react with aldehydes Mg H δ– R δ+ R' C diethyl ether CH3(CH2)4CH2Br H R C R' diethyl ether CH3(CH2)4CH2MgBr H 3C + MgX •• O •• •• – MgX O •• •• H3O+ C H C R product is a secondary alcohol R' H3O+ CH3(CH2)4CH2CHCH3 CH3(CH2)4CH2CHCH3 OH • OH • •• OMgBr (84%) Grignard reagents react with: formaldehyde to give primary alcohols aldehydes to give secondary alcohols ketones to give tertiary alcohols Example Grignard reagents react with ketones Mg R" δ– R δ+ R' C diethyl ether CH3Cl R" R C •• O •• •• – MgX O •• •• R' + H3O+ product is a tertiary alcohol diethyl ether CH3MgCl O MgX HO CH3 R" R C • OH • •• O H R' (62%) H3O+ ClMgO CH3 Preparation of Alcohols From Epoxides Reaction of Grignard Reagents with Epoxides R MgX CH2 H 2C O CH2 CH3(CH2)4CH2MgBr + H2C R CH2 Example O CH2 OMgX H3O+ RCH2CH2OH 1. diethyl ether 2. H3O+ CH3(CH2)4CH2CH2CH2OH (71%) Preparation of Ketones From Acid Chlorides and Grignard Reagents & Preparation of Tertiary Alcohols From Esters and Grignard Reagents Acid Chlorides → Ketones Esters → 3o Alcohols Step 1 Esters → 3o Alcohols Step 2 Grignard reagents react with esters δ– R' R •• R' diethyl ether δ+ OCH3 •• C Grignard reagents react with esters R C •• OCH3 •• • • + MgX •O • •• – MgX O •• •• but species formed is unstable and dissociates under the reaction conditions to form a ketone Example δ– R' R •• δ+ OCH3 •• C R' diethyl ether R MgX O •• •• this ketone then goes on to react with a second mole of the Grignard reagent to give a tertiary alcohol C •• • • + MgX •O • •• – –CH3OMgX R C R' O •• •• O CHCOCH3 2 CH3MgBr + (CH3)2CHCOCH 1. diethyl ether Retrosynthetic Analysis 2. H3O+ Two of the groups attached to the tertiary carbon come from the Grignard reagent OH (CH3)2CHCCH CHCCH3 CH3 (73%) Retrosynthetic analysis is the process by which we plan a synthesis by reasoning backward from the desired product (the "target molecule"). Retrosynthetic Analysis of Alcohols Retrosynthetic Analysis of Alcohols C C OH OH Step 1 Locate the carbon that bears the hydroxyl group. •• OCH3 Step 2 Disconnect one of the groups attached to this carbon. Retrosynthetic Analysis of Alcohols Retrosynthetic Analysis of Alcohols MgX C C OH O What remains is the combination of Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound that can be used to prepare the alcohol. Example C There are two other possibilities. Can you see them? Synthesis CH3 CH2CH3 Mg, Mg, diethyl ether CH3Br CH3MgBr MgBr OH O 1. 2. H3O+ CH3MgX CH3 O C C C CH2CH3 CH2CH3 OH Example H 2C O CHLi + Synthesis of Alcohols Using Organolithium Reagents Organolithium reagents react with aldehydes and ketones in the same way that Grignard reagents do. CH 1. diethyl ether 2. H3O+ CHCH OH (76%) CH2 CH2CH3