* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Common aldehydes and ketones
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
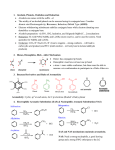
Organic chemistry for medicine and biology students Chem 2311 Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones By Prof. Dr. Adel M. Awadallah Islamic University of Gaza 1 2 3 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Common aldehydes O H O H Methanl (formaldehyde) H3C O O H CH3CH2 ethanl (acetaldehyde) H propanal (propionaldehyde) CH3CH2CH2 butanal (n-butyraldehyde) O O H O H H H OH OMe benzaldehyde salicylaldehyde (2-hydroxybenzenecarbaldehyde) O H 4 cyclopentanecarbaldehyde OH Vanillin Common Ketones O O CH3 H3C propanone (acetone) O cyclohexanone 5 H3C O CH3 CH3 H3C 2-butanone 3-pentanone (ethyl methyl ketone) (diethyl ketone) H3C O acetophenone (methyl phenyl ketone) O benzophenone (diphenyl ketone) Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones (al) aldehyde, (one) ketone alkanes < alkenes < OH < ketone < aldehyde < acid < ester Examples CH3 CH3 3 4 1 2 5 O CH3 H 2 O H3C 3 1 4 Cl 2,4-dimethyl-3-hexanone 2-cholro-3-methylbutanal OH 5 4 3 O O 2 H 1 1 64-hydroxy-2-pentanone 6 O 3 CH3 2 4 3-oxobutanl 6 5 3 2 4 1 CH3 O 3-hexen-2-one 7 Acyl groups 8 Common aldehydes and ketones Formaldehyde CH3OH Ag 600 - 700 CH2 = O oC + H2 Formaldehyde is a gas (b. p. -21 oC) Formalin (37% aqueous solution of formaldehyde) Acetaldehyde (Wacker synthesis) Pd - Cu 2 CH2 = CH2 + 2 CH3CH = O O2 100 - 130 oC (bp 20 oC) Acetone (Wacker synthesis) O Pd - Cu 2 CH3 C CH3 2 CH3CH2 = CH2 + O2 100 - 130 oC (bp 56 oC) From isopropylbenzene OH O 1) O2 9 2) dil H2SO4 + H3C CH3 Synthesis of aldehydes and Ketones 1) 2) Oxidation of Alcohols primary gives aldehydes using PCC secondery gives ketones Friedel-Crafts CH3COCl AlCl3 3) 10 From Alkynes H3C O Naturally occuring aldehydes and Ketones 11 The carbonyl group 12 Reactions of the carbonyl group 13 A. Hydration and Hemiacetal Formation • • • • • Water adds rapidly to the carbonyl function of aldehydes and ketones. In most cases the resulting hydrate (a geminal-diol) is unstable relative to the reactants and cannot be isolated. Exceptions to this rule exist, one being formaldehyde (a gas in its pure monomeric state). Thus, a solution of formaldehyde in water (formalin) is almost exclusively the hydrate, or polymers of the hydrate. Another is chloral hydrate OH CCl3 14 OH H Chloral hydrate Addition of Alcohols 15 Examples 16 17 18 Addition of hydrogen cyanide to aldehydes and ketones 19 Addition of sodium hydrogensulphite to aldehydes and ketones • 20 Uses of the reaction The reaction is usually used during the purification of aldehydes (and any ketones that it works for). The addition compound can be split easily to regenerate the aldehyde or ketone by treating it with either dilute acid or dilute alkali. Reducing Agents The reduction of an aldehyde You get exactly the same organic product whether you use lithium tetrahydridoaluminate or sodium tetrahydridoborate. For example, with ethanal you get ethanol: 21 The reduction of a ketone • Again the product is the same whichever of the two reducing agents you use. • For example, with propanone you get propan-2-ol: • Reduction of a ketone leads to a secondary alcohol. 22 Mechanism of reduction 23 • Using sodium tetrahydridoborate (sodium borohydride) . • Sodium tetrahydridoborate is a more gentle (and therefore safer) reagent than lithium tetrahydridoaluminate. It can be used in solution in alcohols or even solution in water - provided the solution is alkaline 24 25 REACTION OF ALDEHYDES AND KETONES WITH GRIGNARD REAGENTS 26 The reaction between Grignard reagents and methanal 1) EtMgBr 2) H2O, H+ The reaction between Grignard reagents and other aldehydes 1) EtMgBr 2) H2O, H+ The reaction between Grignard reagents and ketones 1) EtMgBr 2) H2O, H+ 27 28 Reaction with Acetylides 29 OXIDATION OF ALDEHYDES AND KETONES 30 ADDITION-ELIMINATION REACTIONS OF ALDEHYDES AND KETONES 31 32 with hydroxylamine The product is an "oxime" - for example, ethanal oxime. 33 Formation of Imines and Related Compounds The reaction of aldehydes and ketones with ammonia or 1ºamines forms imine derivatives, also known as Schiff bases, (compounds having a C=N function). 34 Keto-Enol Tautomerism • Keto-enol tautomerism a neewteb muirbiliuqe lacimehc a ot srefer keto na dna )edyhedla na ro enotek a( mrof enol dna lone ehT . ehT .rehto hcae fo sremotuat eb ot dias era smrof otek notorp a fo tnemevom eht sevlovni smrof owt eht fo noisrevnocretni seifilauq msiremosi eht ,ecneh ;snortcele gnidnob fo gnitfihs eht dna .msiremotuat sa • A compound containing a carbonyl group (C=O) is normally in rapid equilibrium with an enol tautomer, which contains a pair of doubly bonded carbon atoms adjacent to a hydroxyl (−OH) group, C=C-OH. The keto form predominates at equilibrium for most ketones. Nonetheless, the enol form is important for some reactions. Furthermore, the deprotonated intermediate in the interconversion of the two forms, referred to as an enolate anion, is important in carbonyl chemistry, in large part because it is a strong nucleophile. 35 36 Acidity of α-Hydrogen 37 • Examples of -Hydrogen exchange 38 The Aldol Condensation The name aldol is derived from "aldehyde" and "alcohol". An aldol is a β-hydroxycarbonyl compound. 39 40 41