* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The carbonyl group
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Carbohydrate wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
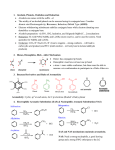
The carbonyl group • The carbonyl group (C=O) is found in aldehydes, ketones, and many other organic functional groups. • In ketones, two carbon groups are attached to the carbonyl carbon. • While in aldehydes at least one hydrogen is attached to the carbon. Aliphatic formaldehyde Aldehydes Aromatic Benzaldehyde Acetone Ketones Aliphatic Aromatic Acetophenone Physical properties • The carbonyl group is a strong dipole. This causes the B.P of aldehydes and ketones to be higher than similar molecular weight alkanes and others but lower than alcohols which are held together by H-bonds. Aldehyde < Alcohols > Alkane Solubility • Because aldehydes have an O atom, they can H-Bond with water. They are about as soluble in water as alcohols of comparable weight. Chemical Properties 1. 2,4 Dinitrophenyl hydrazine test • Aldehydes and ketones react with a number of nitrogen containing compounds through nucleophilic addition and subsequent loss of water to give products that have a carbon nitrogen double bond. These reactions are useful in distinguishing an aldehyde or ketone from other functional groups. (General test) NO2 NO2 R + C O +H2N NH R aldehyde or ketone 2,4 NO2 dinitrophenylhydrazine +ve result yellow ppt H R C N NH R 2,4 dinitrophenylhydrazone NO2 2. Tollen’s test • Aldehydes are very easily oxidized to yield carboxylic acids or their salts if the reaction is done in basic media. • This test is a useful method of differentiating between aldehydes and ketones. • The silver ion is reduced to metallic silver in a positive reaction. RCHO + 2Ag(NH3)2OH 2Ag(s) + RCOO-NH4+ + H2O + NH3 3. Fehling’s test • To distinguish aliphatic from aromatic aldehydes. O R C H + 2Cu+2 + 5 HOBlue solution O R C O- + Cu+2 Red ppt 4. Iodoform test • Ketones can be distinguish by their reaction with iodine in a basic solution to yield iodoform as a yellow colored ppt.