* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric hydrogenation wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogenation wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
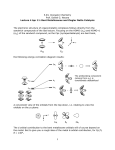
Lecture 38 Organometallic reactions and catalysis 1) Catalytic olefin hydroformylation. Monsanto acetic acid process • • Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across olefinic C=C bond to form linear and branched aldehydes: H Me • • • • C H CH2 CO, H2 cat Me H C H H2 C C H linear H2C O formyl + O Me C C H H branched RhH(CO)L 3 (Union Carbide, Hoechst, BASF) HCo(CO) 4 (Exxon, BASF) HCo(CO) 4-n(L)n (Exxon, BASF) Olefin hydroformylation is used in industry for multimillion ton annual production of aldehydes (butanal, in particular). The HCo(CO)4 – catalyzed hydroformylation was discovered in 1938 (Otto Roelen). Its mechanism was suggested in 1960-s. O carboxyl H H2 Aldehydes formed in Me C C C hydrocarboxylation O hydroformylation reaction OH , H2 H O C can react with H2 to produce O alkoxycarbonyl H H2 primary alcohols. Me C CH2 CO, HOR Me C C C hydroalkoxycarbonylation H C OR O H Later a number of other ,H N R carbonylation reactions was 2 O H H2 amidocarbonyl hydroamidocarbonylation discovered (see scheme). Me C C C H NR2 2) Mechanism of the catalytic olefin hydroformylation by HCo(CO)4 • • • • • • 2 +H • The currently accepted mechanism of olefin hydroformylation by HCo(CO)4 is given below. The catalyst, A, forms readily from Co2(CO)8 and H2 (100oC, up to 100 atm of CO and H2). Subsequent ligand exchange leads to olefin complex B where C=C bond is “activated” due to coordination to cobalt atom. H Insertion -CO OC O H of olefin into Co-H Co CO OC bond leads to OC H A H Co CO alkylcobalt C. OC O +C Subsequent insertion linear / branched 3 : 1 +H2 CO B of CO into Co-C bond CO O produces acylcobalt D. H H +CO CO OC Co O The rate limiting step is CO H OC H oxidative addition of H2 to Co CO OC C H OC acylcobalt D to produce Co E OC H CO dihydride E and to transform OC CO Co CO strong H-H bond into two OC weaker Co-H bonds. D CO -C O O Subsequent reductive slow O +C branched isomer elimination of aldehyde also forms H H OC and coordination of CO Co CO OC regenerates the active OC Co CO OC species A. CO CO 3) Modified catalysts for olefin hydroformylation • • • Co – phosphine modified catalysts. Studies performed at Shell showed that addition of trialkylphosphine ligands changes dramatically the reaction rate and selectivity. When HCo(CO)3(PR3) forms, Co-CO bonds become much stronger and it becomes possible to decrease CO pressure without causing catalyst decomposition. becomes stronger Bulkier PR3 favor greater linear / branched becomes more hydride-like H aldehyde ratios ( up to 8 : 1). CO Finally, more hydride-like Co-H promotes aldehyde OC Co hydrogenation to alcohols: CO O R H2 PR3 H2 C OH R strong -donor H • • Further studies allowed to establish that Rh analogues such as HRh(CO)(PPh3)3 are 103-104 times more active in olefin hydroformylation so that it can be performed at ambient pressure of H2 and CO and room temperature. This catalyst favors also greater linear to branched aldehydes ratio (up to 20 :1). The reaction mechanism is similar to that with HCo(CO)4. HRh(CO)(PPh3)2 is considered as catalytically active species. H OC PPh3 Rh PPh3 - PPh3 OC Ph3P Rh PPh3 H PPh3 • Currently a number of more sophisticated modifications of the olefin hydroformylation catalysts are known which also allow to perform olefin hydroformylation stereospecifically. 4) Monsanto acetic acid process: MeOH + CO MeCOOH • • This is another carbonylation reaction introduced in early 70-s by Monsanto. This reaction involves dual catalysis with HI and with salts of [RhI2(CO)2]- anionic complex. Hydrogen iodide is responsible for conversion of MeOH into MeI. Rhodium catalyst is responsible for carbonylation of MeI into MeCO-I. Finally, HI is regenerated in the end of Rh-catalytic cycle as a result of hydrolysis of acetyliodide. Me O C OH OC I MeOH Rh CO I Me-I Me OC I Rh CO I I Me O C reductive elimination migratory insertion Me Me I CO OC I Rh I C I O CO OC I Rh I C I O